How to Recover Data after a Ransomware Attack
- Overview
- Prerequisites
- Phases of a Cyber Incident
- Technologies & Capabilities You need to Have In-place
- When to start data recovery after a Ransomware Attack
- How to recover data after a Ransomware Attack
Overview
The steps in this topic cover the process to follow when recovery from a large scale Ransomware Attack or other similar attack.
Prerequisites
- Best Practice
- Deploy an Airgap to protect versions of your data in an offline protected cyber vault. See the Ransomware Defender Enterprise Airgap 2.0 guide.
- Forensics tools to determine the beginning of the attack. Easy Auditor provides historical user behavior searching to provide input to the forensic research to determine the beginning of the attack. Other security tools should be used in addition to audit data to determine when and where the initial attack began and what additional systems may have been compromised.
- Ransomware Defender's CSV files will provide input to the security team research. Collect the list of users from Ransomware Defender that need further analysis in Active Directory and other systems these users had access to and assess damage to other systems, applications, file systems.
- Easy Auditor provides interactive search by user or path to narrow down where in the file system the attack was initiated.
- Correlate time stamps with network security logs and SEIM tools to identify where the threat originated within the infrastructure.
- Compile a compromised systems list of servers, users, file system paths for a complete forensic analysis of the impact.
- Quarantine comprised data for AV scanning and root cause of infection. Cyber Recover Manager allows automated data recovery and quarantine for this reason. See procedures here.
Phases of a Cyber Incident
Detection - We have a problem!!
How will we know we have a problem with our data?
Security tools raised an event?
A user raised the issue?
Identify - What is the scope of the incident file system, object storage.
Is the attack still happening now?
Did we sync the problem from file to object?
Did we backup the data?
What data is impacted (file and object)?
Which user accounts?
Which subnets?
Which systems are affected?
Response/Protection - How to stop an attacker; Remember attackers want your data!!
Stop file services and object services (stop the business)
Shut off the Internet connection
Recover - Where do I start?
Forensics, forensics, Forensics - If you don’t know who, what, where and how. It is hard to recover effectively.
Do we have auditing tools for file systems and object storage systems?
How far back do we store forensic logs?
Do you have offline backups?
How to determine the fastest , safest method to recover
Technologies & Capabilities You need to Have In-place
Capability | Why it’s Important | Phase of Cyber Event | How to Address? |
File system auditing | Forensics and detection of possible data attack | Detection, Identification, Recover Forensics | Onefs file Auditing |
Object data access monitoring | Forensics and detection of possible data attack | Detection, Identification, Recover Forensics | ECS web access log forwarding |
IDS & IPS network systems | Early warning system and key detection vector | Detection, Identification | Zero Trust API from Superna |
Endpoint protection on all client machines & servers that touch data | Early warning system and key detection vector | Detection, Identification | Ransomware Defender, Easy Auditor (ECS and PowerScale) |
Snapshot features for file systems | Recovery tool | Recovery | Onefs Snapshots, ECS bucket versioning and object lock |
Object lock capabilities for object storage with versioning | Recovery tool | Protection | ECS object lock + Versioning |
Backup | Slow Recovery tool | Recovery | Golden Copy |
Cyber Vault (offline data) | Rapid Recovery tool | Business continuity | PowerScale and ECS Cyber Vault Airgap Solution |
When to start data recovery after a Ransomware Attack
Many steps should be completed before starting any data recovery steps. These steps would be completed by the Senior Security team members with input from the Storage team that has forensic input data needed to complete the process.
- Inspect all of the IT infrastructure to verify impact and no remaining threat exists in the environment. Example Active Directory, DNS, application servers, desktop PC's and any other system required for normal IT operations.
- The chief security officer or similar role within your Enterprise should declare a data recovery start phase. This phase may not start for many days depending on how long the security audit of the safety of the infrastructure takes to complete.
- The Chief Security officer team should provide the summary of the compromised systems list and the ordering of the recovery effort.
- The applications servers, infrastructure are first priority
- Data recovery should not begin until the application servers and infrastructure (AD , DNS, NTP) recovery is completed.
- User workstations would be last in the recovery effort
- Until this phase has been declared by senior security management within your company no data recovery should be attempted. The risk of data being attacked again from a persistent active threat will increase your recovery phase.
- Ransomware Defender users in lockout state should remain in this state until the recovery phase is completed and the infected PC's or VM's have been remediated.
- Identify the time stamp of the initial attack to use in recovery from Ransomware Defender CSV files and snapshots or leverage Airgap data protected by Ransomware Defender.
How to recover data after a Ransomware Attack
- To begin the data recovery phase start to build a list of snapshots with creation time stamps in a document.
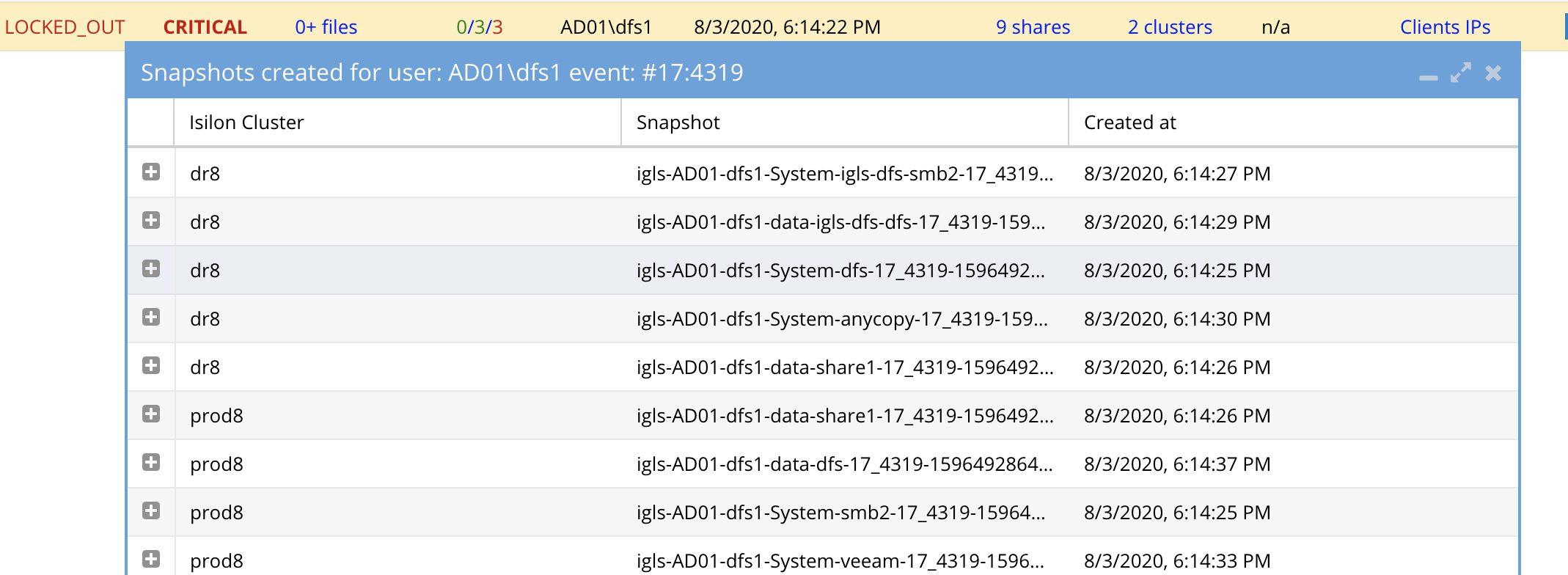
- Login to Ransomware Defender open the active events tab and open the snapshots list for each locked out user and record the date and time stamps of each SMB share. Example below.
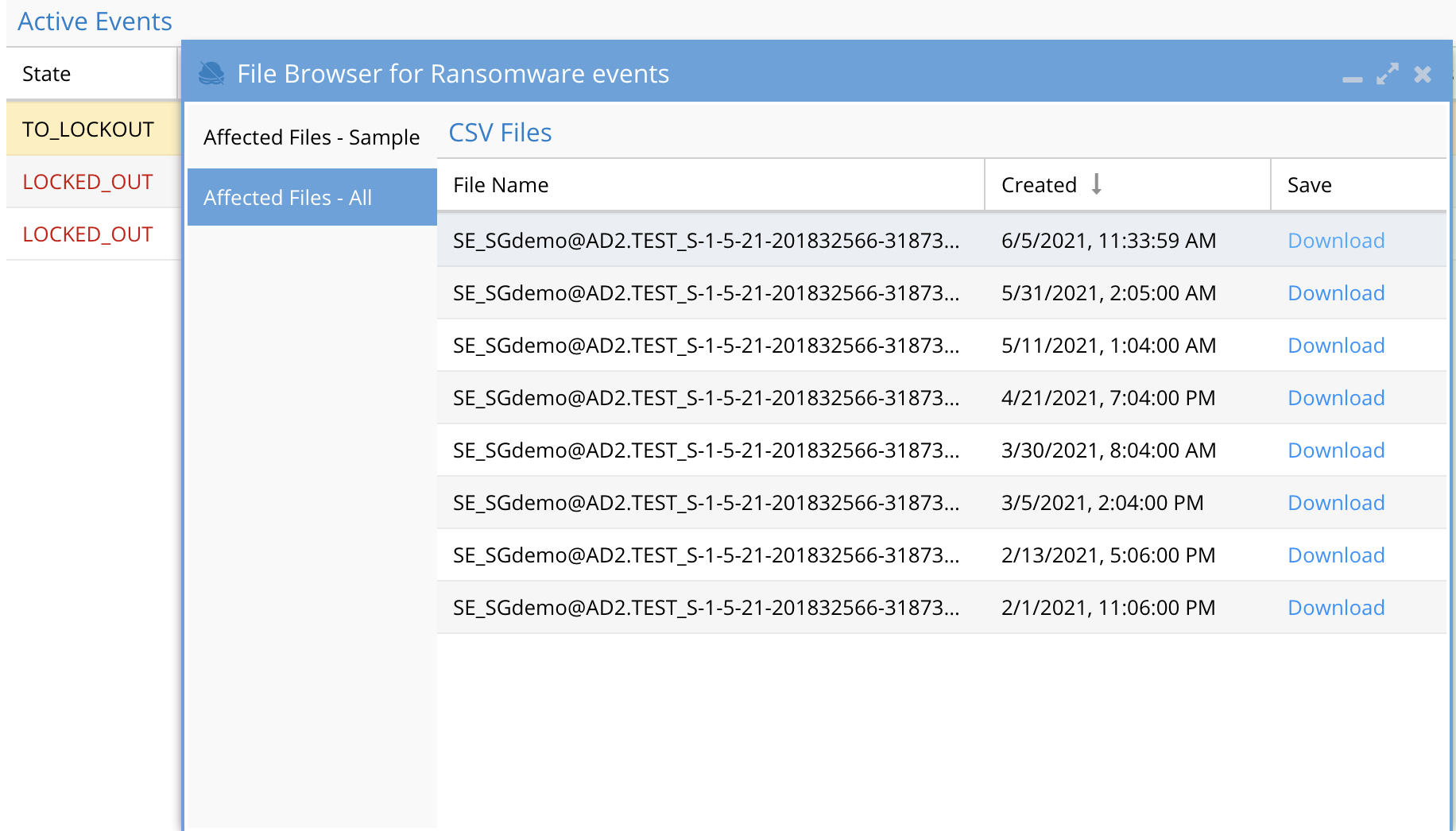
- For each locked out user view the most file data associated to event summary by browsing the tree view. The CSV is is only a sample of the activity for this user. See the next step for detailed forensics.
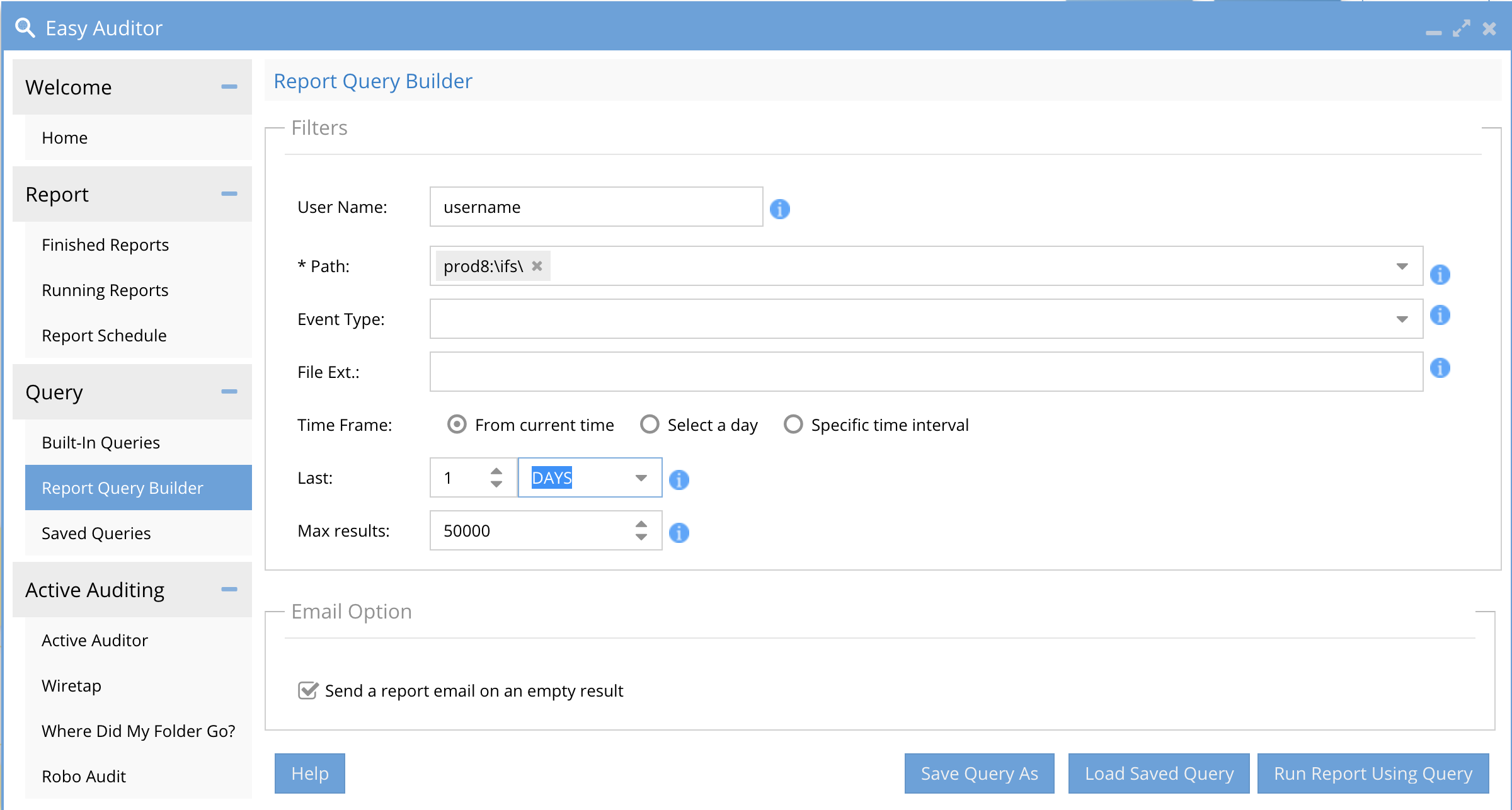
- The Defender CSV files contain the first 1000 files of the users activity during the attack. To get a more precise list of files including files the user touched prior to the detection an Easy Auditor user report can be run using /ifs/ path and last 24 hours for the search. Example below. Easy Auditor supports upto 1 million file csv download and is designed to provide more precise searching and export of information into a CSV for forensic investigations.
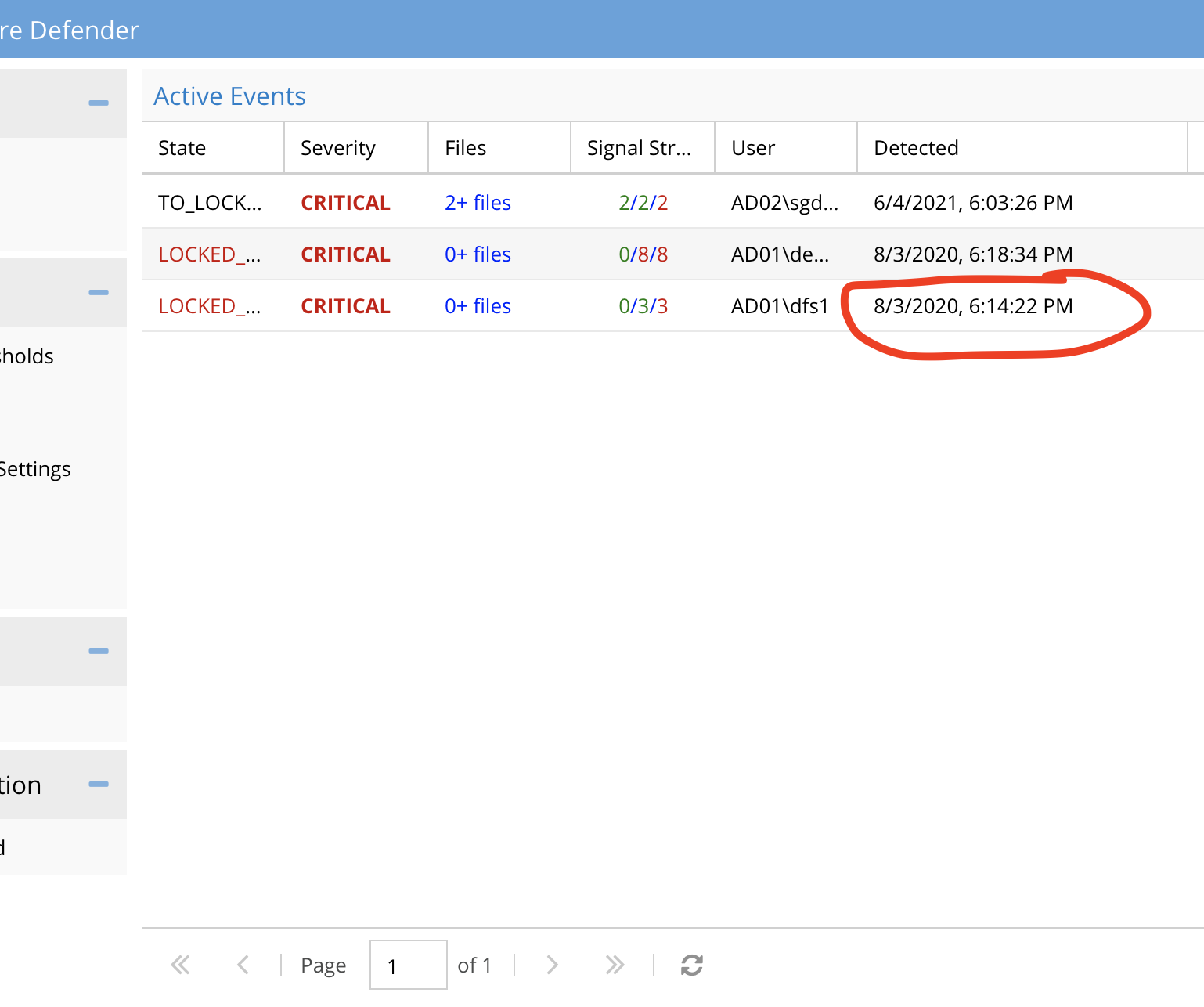
- Using the CSV files and Easy Auditor reports review the absolute path of the files and user the snapshots taken from the first user that was detected. This user will have the oldest detection time in the active events window. See example below.
- Using the snapshot list from this procedure browse to the snapshots listed for user one and use this snapshot to restore the files in the CSV by dragging the files from the snapshot back into the file system. Repeat these steps for each file in the CSV or Easy Auditor CSV report for each user.
- NOTE: A visual inspection of the file system where data is being restored should be done during this process. You may delete any encrypted files that are found in the file system or store data for analysis later.
- For follow analysis an administrator only SMB share can be created for a post mortem and encrypted files can be moved to this SMB share. These files should be reviewed by security personnel before deletion.
- NOTE: You may find ransomware notes or possible other strange or unidentifiable file types , these files should be moved to the port mortem SMB share for further analysis by security personnel.
- NOTE: After completing the post mortem and data recovery the encrypted/compromised files should be deleted.
- NOTE: A visual inspection of the file system where data is being restored should be done during this process. You may delete any encrypted files that are found in the file system or store data for analysis later.
- Unlocking Locked Users - This should require approval from the CSO or similar senior management. Follow the procedures here.
- Done