Planning and Design
- Overview
- Automated Ransomware Defense Actions
- Securing Root user on PowerScale
- Why file extension filtering feature on SMB shares is a security risk
- External Data Security Expectations for A Secure Environment
- How to determine threat response settings to meet your Company’s Risk Profile
- Eyeglass User Lockout Active Directory Planning
- Ransomware Audit Events Required for all Deployments
- Well Known Ransomware File Extension Whitelist
- Security Event Descriptions
- NFS Lockout Feature
- Planning New application Workloads Best Practice
Overview
The Ransomware Defender solution for PowerScale requires existing Eyeglass DR cluster licenses for each PowerScale cluster plus, an Eyeglass clustered agent license.
The Eyeglass Ransomware Defender solution is intended to be a last line of defense for critical NAS data stored on PowerScale. A best practice defense should include virus software on laptops and workstations, along with email gateway or IDS network solutions.
For Dell ECS, Ransomware Defender can monitor object access with behavior based detection and offers alerting and lockout of authenticated users.
The intended use case for Ransomware Defender assumes malware has circumvented all existing defenses, leaving critical NAS and object data exposed to attack.
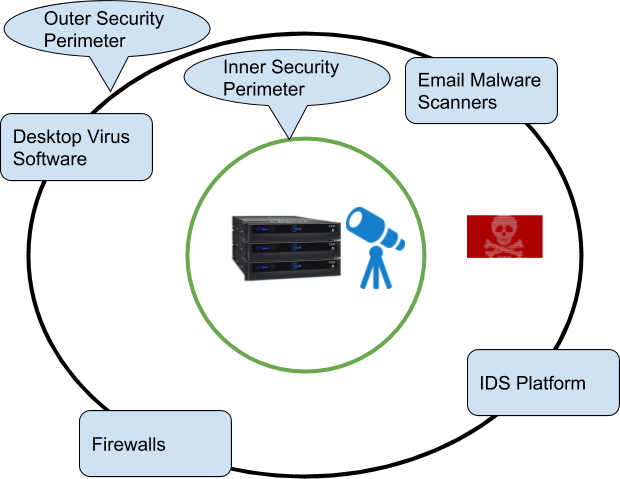
The diagram below shows the traditional approach to security with perimeter defenses, with the primary purpose of ensuring malware never enters your network.
The Eyeglass solution builds a new security perimeter inside your network with active defense to threats.
Automated Ransomware Defense Actions
- Warning - Send an alert (email, snmp, syslog), no enforcement taken.
- Timed lockout (Major) - a time-delayed lockout of the user account that triggered the security event. The lockout can be stopped before the timer expires.
- Immediate lockout (Critical) - User lockout begins in real-time once a critical event is detected.
- Snapshot the file system (all severities) using SnapshotIQ on all affected share paths. (Isilon/Powerscale only)
Securing Root user on PowerScale
The root user should never be used to access data on PowerScale. The reason this user is a high-security risk is that root has access to all shares even if access has not been granted to the root user. This security risk could allow a compromised machine, using the root user, to access data and could encrypt all data on the cluster.
Eyeglass Ransomware Defender offers a mode configured through IGLS CLI to disable SMB protocol on the PowerScale clusters managed by Eyeglass. This will ensure if a ransomware event is detected the compromised machine does not destroy all data on all clusters. See Eyeglass CLI command for Ransomware .
The root user can NOT be locked out with a deny permission, which is why SMB protocol disable is the only way to protect data.
NOTE: IF YOU USE RUN AS ROOT ON SHARES YOU ARE EXPOSING DATA TO VERY HIGH SECURITY RISK SINCE NO LOCKOUT WILL BE POSSIBLE. THIS IS BECAUSE THE USER SID, THAT IS SENT WHEN AN AD USER ACCESSES DATA WITH RUN AS ROOT ENABLED, IS THE ROOT USER NOT THE ACTUAL AD USER.
We recommend to NOT use run as root on shares for the reason above, AND it fails all security audits of PowerScale in all industry standards (PCI, HIPPA, FedRAMP, ITSG, etc…). Remove run as root option on all shares.
The default setting is to disable the SMB Automated response on a cluster if the root user SID has tripped a threat detector. To enable this mode VERIFY no run as root user shares exist.
This can be done using the Eyeglass cluster configuration report
- Login to Eyeglass
- Open Reports on Demand Icon
- Select Create New Report

- Wait until the report is finished by viewing running jobs
- Select Open/Print option for the finished report from Reports on Demand, after running jobs shows the report creation is completed.
- Click Cancel on Print option (if using Chrome).
- Control-F to search the page option
- Search for “run_as_root”
- If any Shares are found with this option set see below.
- DO NOT ENABLE LOCK ROOT FEATURE.
Why file extension filtering feature on SMB shares is a security risk
- This Isilon feature changes the audit events created which means Ransomware Defender will not be able to "see" the active ransomware attack and no alert will be sent since isilon suppressed the audit data.
- This means you will blind to an active Ransomware attack based on the blocked extension added to the SMB shares.
- NOTE Ransomware Defenders primary detection vector is user behavior
- In 2.5.7 or later you can customize the banned file list and is the recommended method to add banned file extensions since each extension can be enabled (protection active), disabled (added but no active monitoring) or monitor mode that will alert but will not lock out users. These 3 states provides more options than the blocking only.
External Data Security Expectations for A Secure Environment
- Ransomware Defender is a component of an overall security solution that must include the following best practices in order to correctly deploy a security solution.
- A data security plan should include multiple layers of security including end point protection and a backup system to recover data. Ransomware Defender is not intended to replace other security solutions or backups of your data.
- Backup data should be stored off line so that is is not connected to a network.
- Offline copy of data using a cyber vault or airgap.
- Dedicated virtual infrastructure for Ransomware Defender VM's
- As a best practice, dedicated highly located own vmware infrastructure is recommended. Bad actors attack vmware hosts, vcenter by placing Ransomware Defender VM's on dedicated secure applications along with other security products to ensure the security products are isolated on separate infrastructure.
- The specification and operational management of this product Requires:
- May not detect or prevent any or all malicious code or that use of the licensed program and related updates or upgrades will keep company’s network or computer systems free from viruses or other malicious or unwanted content or safe from intrusions or other security breaches
- Product usage assumes end point protection Anti-virus software is in place on all operating systems, devices, computers.
- All computers with operating systems are patched regularly and all zero day patches are applied immediately.
- SPAM filters are implemented for phishing attacks
- All CVE's are acted upon with patches and remediation applied
- All firewalls, security devices are running current versions and configured correctly to protect networks
- The compute infrastructure is maintained and provides minimum product requirements for cpu, memory, disk latency.
- The end users and IT are trained to respond to a Ransomware attack and have a run book to respond to an incident.
- End users are trained regularly for phishing attacks and social attacks intended to compromise computers with Malware/Ransomware
- All product alerts are acting on in a timely manner in the infrastructure and patched weekly for all critical security patches.
- Security guard product feature is monitored daily for proper product functionality
- Honeypot feature is implemented fully on all SMB shares and NFS exports