How To Manage False Positives and Learning Mode
- How to Teach Ransomware Defender about false positives - Learning Mode
- How to manually flag a security Event as False Positive
- How to View or Delete a Flag as False Positive User setting
- How to manually configure per-user Threat level settings with IGLS CLI
- Global, Group-Specific and Selected Path Threshold Settings for False Positives
- Enabling Generic Threshold Configuration
- Applying Thresholds
How to Teach Ransomware Defender about false positives - Learning Mode
- Requires: Release 2.5.7 or later
- NOTE: When learning mode is enabled and learning is active a lot of snapshots can be created. Monitor the snapshot usage on your cluster. Snapshots are created with 48 hour expiry by default and will clean up within 2 days.
- Learning Modes
- Full Learning Mode - This mode applies to all security events detected an no lockouts will occur and all security events will be used for learning.
- Monitor mode list Learning Mode - This mode allows both enforcement and learning of monitor mode list entries. In this mode all security events that do Not match a monitor mode learning mode list entry will be enforced and lockouts can occur based on thresholds. For events that match an entry on the monitor mode lists learning will be applied.
- Use Case: Service accounts or new application work loads can be added to the monitor mode list by path, user or server IP address to allow learning mode to automatically configure settings for this workload.
- Full Learning Mode
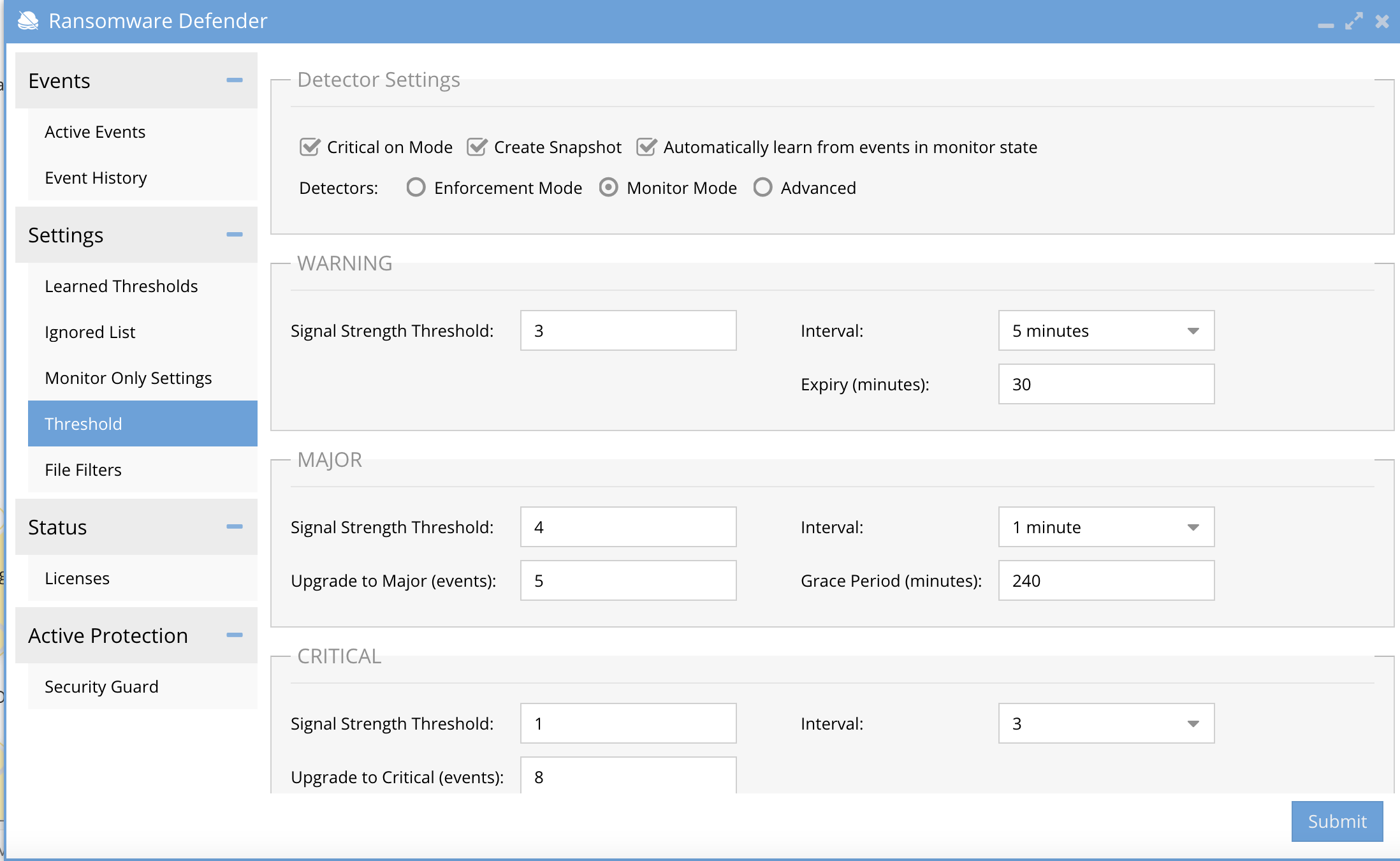
- Enable Monitor mode (settings tab --> Thresholds) to allow user behaviors to be detected without actions taken to lockout.
- Now enable Learning mode from the Thresholds screen once monitor mode is enabled Settings --> Threshold --> click "Automatically learn from events in monitor state". Click submit to save.
- Monitor mode list Learning Mode
- Enable Learning mode from the Thresholds screen once monitor mode is enabled Settings --> Threshold --> click "Automatically learn from events in monitor state". Click submit to save. Example screenshot below.
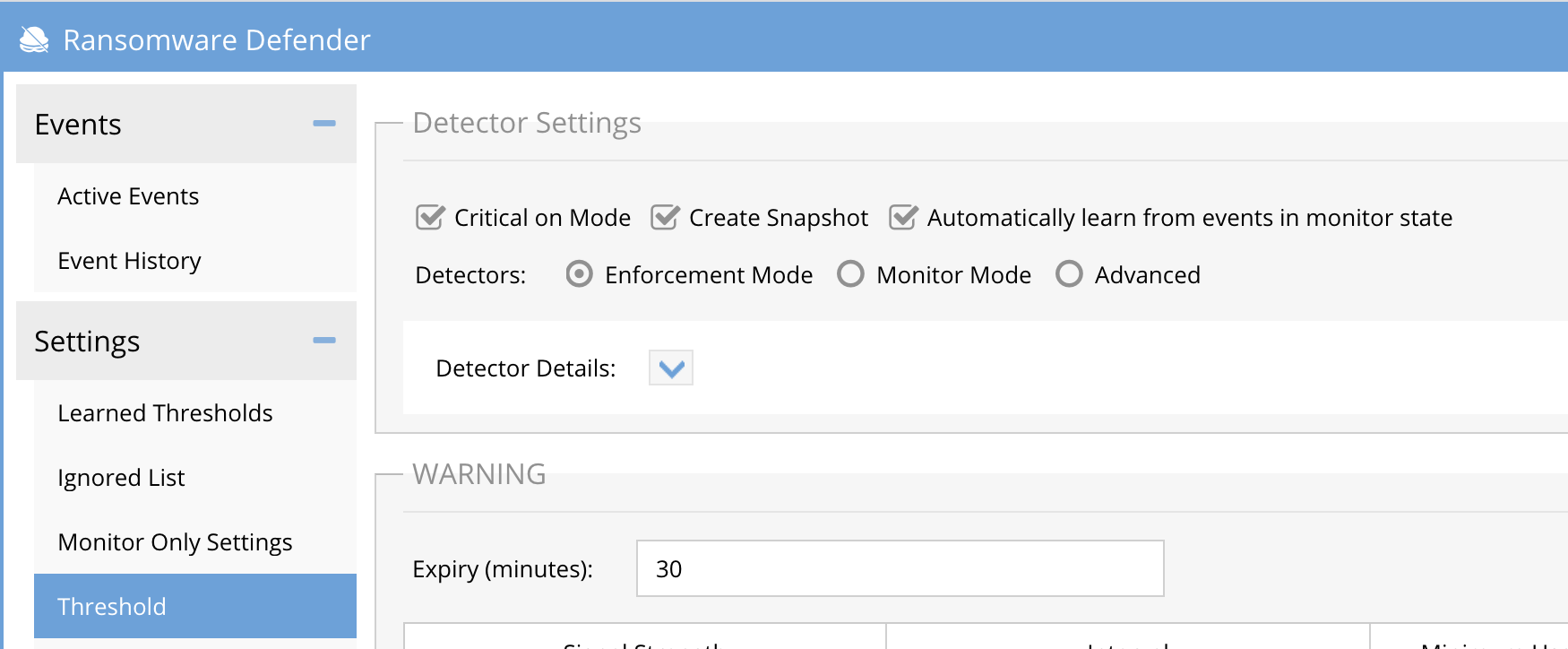
- Leave this enabled for 2-3 business days and monitor the customized user behavior settings on the Learned Thresholds tab.
- This is where Learning mode will place customized settings. It will also set file extension detections on the File Filter tab into a disabled state so this file extension will not be detected as Ransomware.
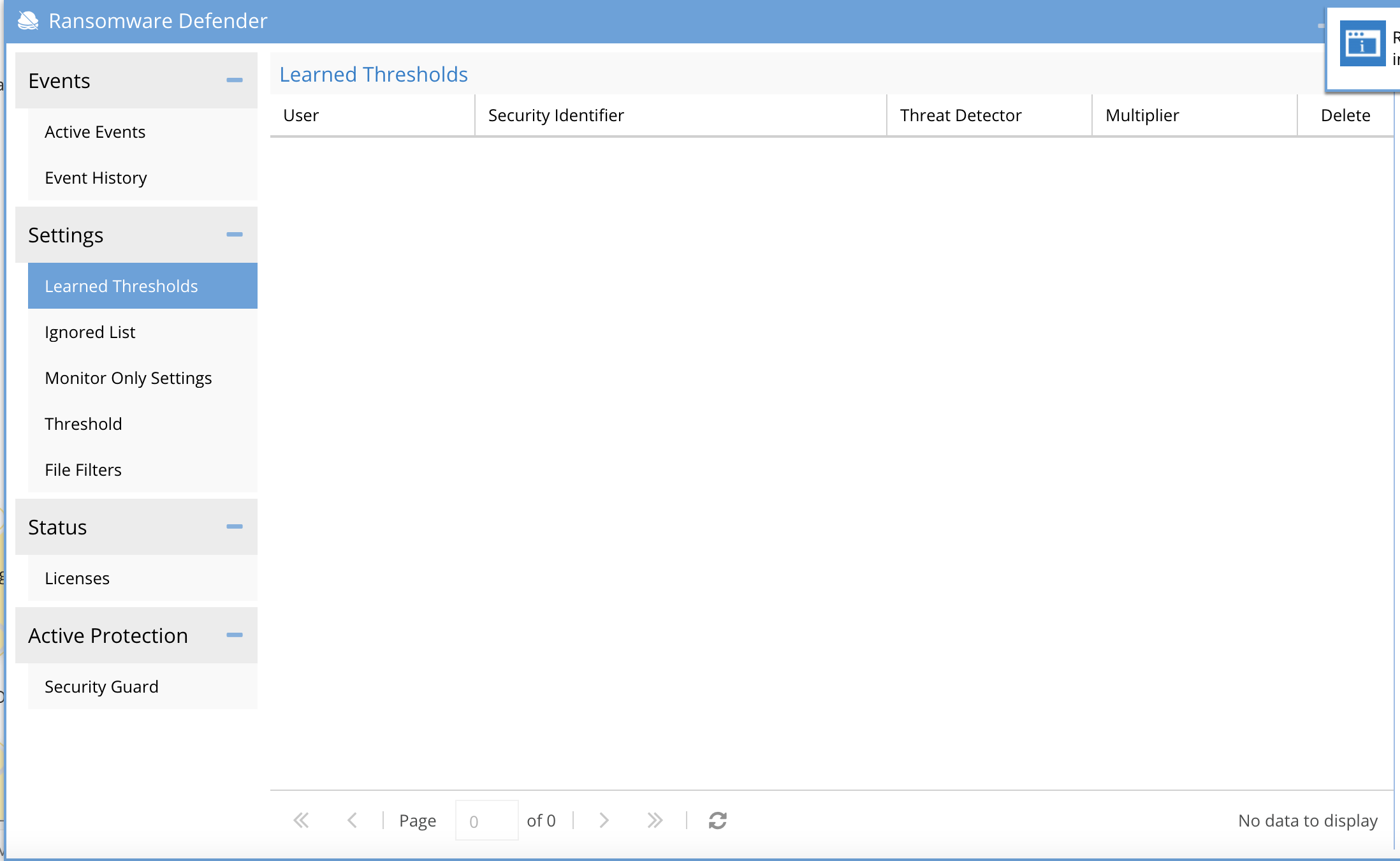
- The process to disable Learning Mode and then enter Enforcement Mode.
- Review user settings on the Learned Thresholds tab to approve the list of users or NFS hosts or delete entries as needed. Consult with support or accept the learned behaviours.
- Review the File Filter list extensions that are disabled status; these extensions have been placed on the Allowed list and will not trigger a detection.
- Use the filter option to locate all the disabled file extensions by entering Disabled in the filter box.
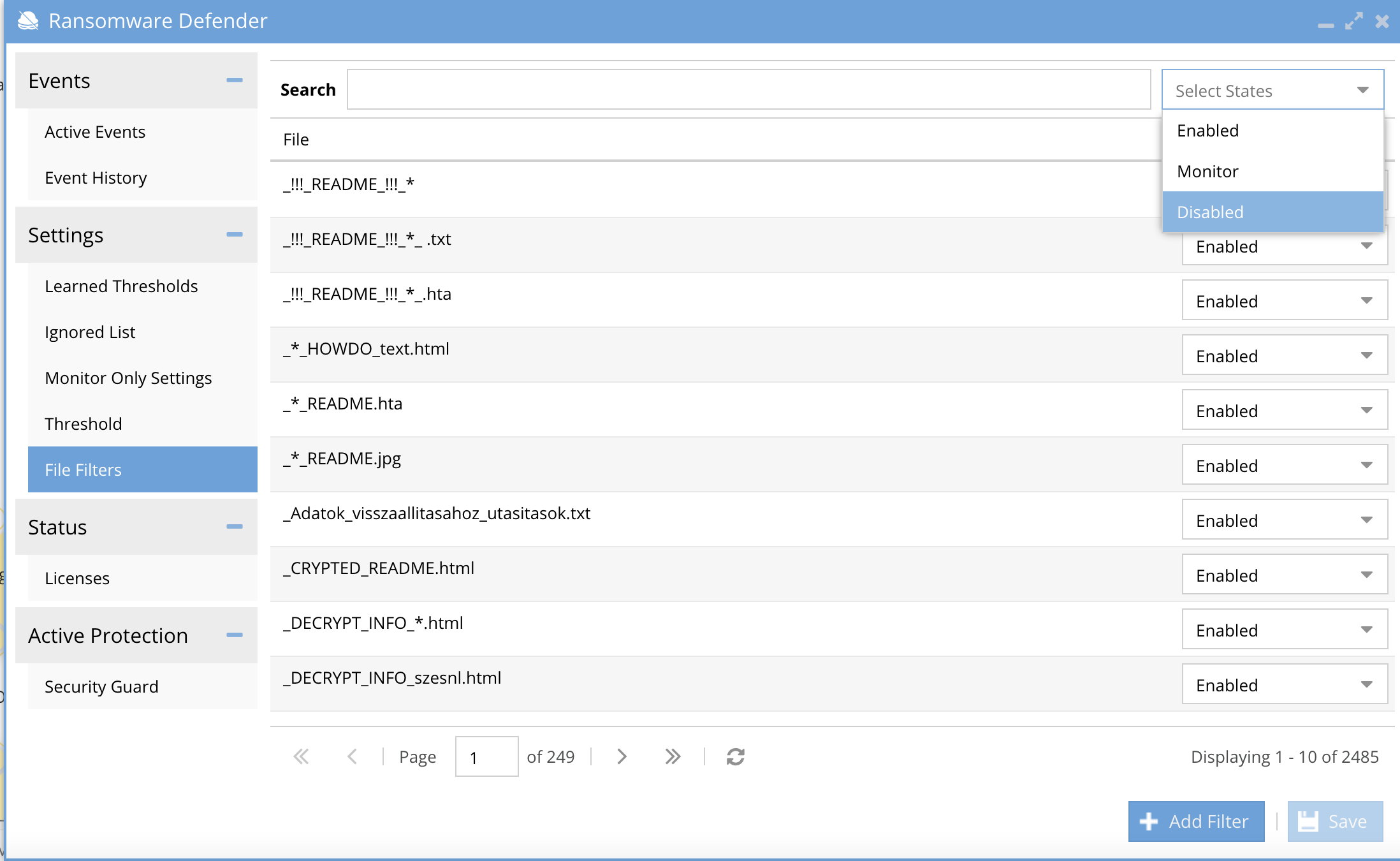
- Review all the extensions that were detected and disabled. If they are acceptable no action needed.
- To change the setting on the extension to enable enforcement and detection of this file extension, you may also chose monitor mode on the file extension to allow detection, snapshot but no lockout for this file extension.
- 3 possible modes for each file extension enabled (full enforcement), disabled (ignored), monitor mode (detect, alert, snapshot and no lockout)
- Disable Learning mode once the file settings are confirmed from the Settings-->Threshold tab and click submit to save. This only disables learning mode and remains in Monitor mode.
- To enter enforce mode mode disable monitor mode from the Settings-->Threshold tab and click submit to enter enforcement mode.
8. Adding a path to learned thresholds (only supported for PowerScale and only after 2.9.0 release )
Here is an example:a. Raise an event (TD 03 by renaming 30 files.)
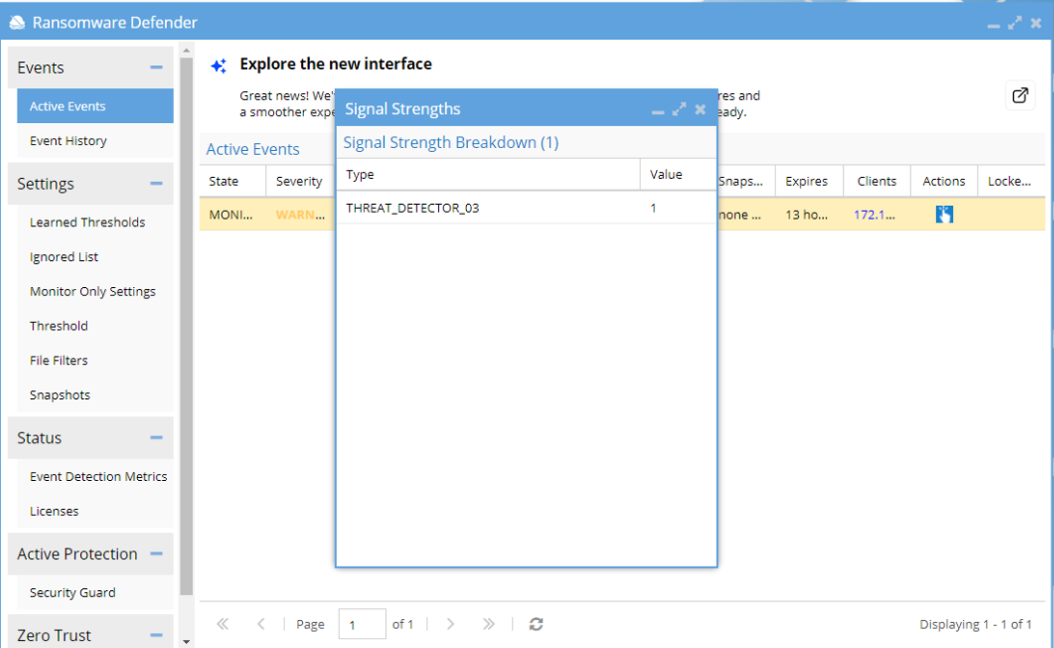
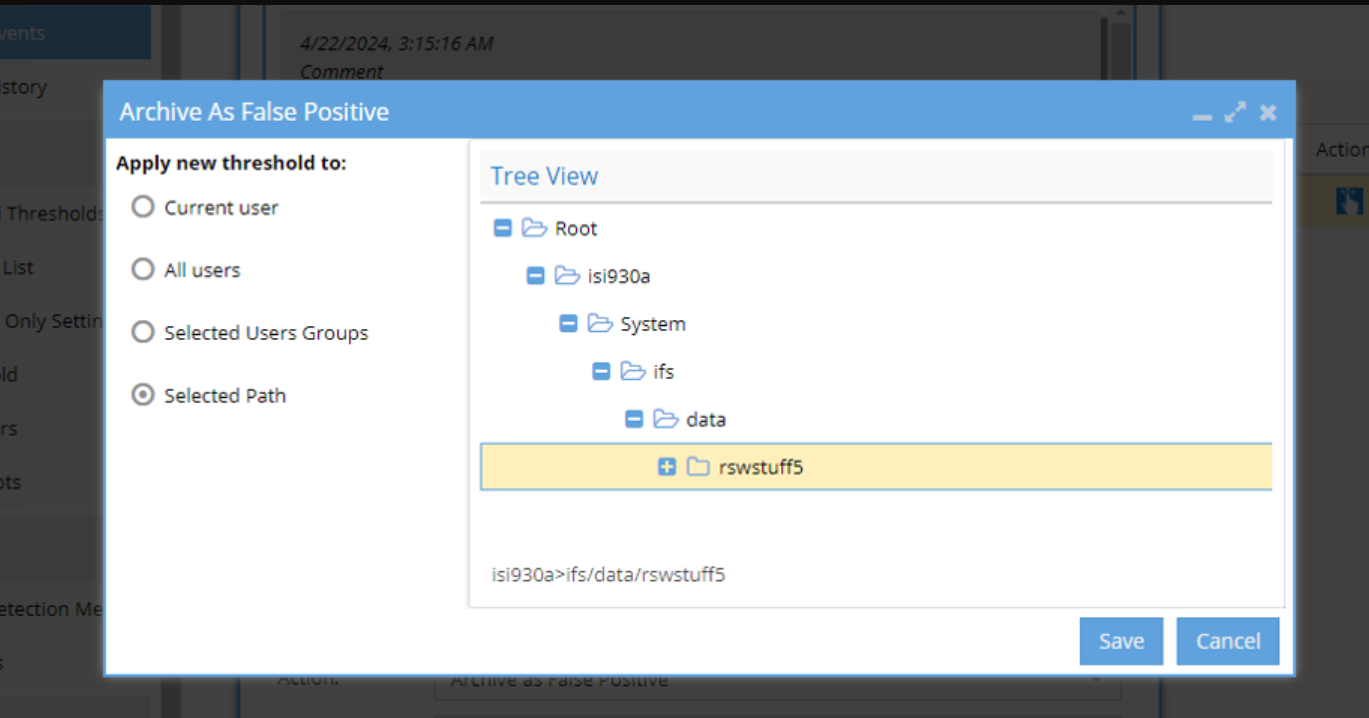
b. Archive it as false positive choosing the path
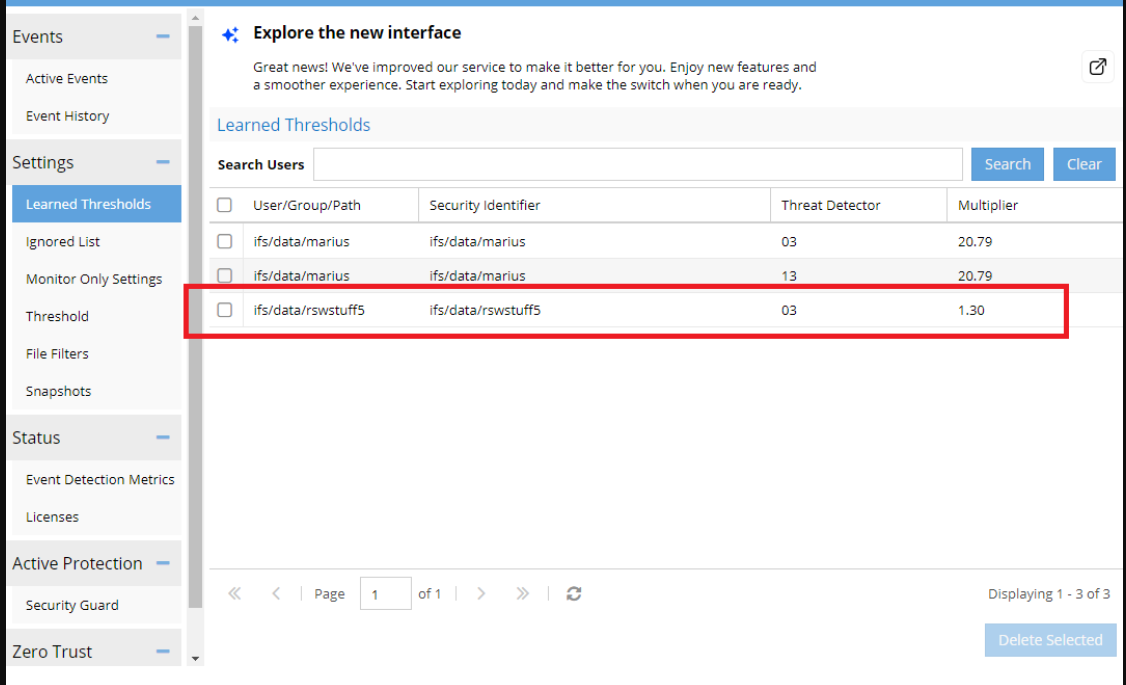
Because no other multiplier existed before on this path, the event was directly archived and new multiplier can be seen:
After waiting some time, tried again to raise the event by renaming 35 files => event was not raised.
tried with 40 files =>Event was raised again.
Flag as false positive with the same path. The user is asked whether to upgrade the multiplier or just archive the event:
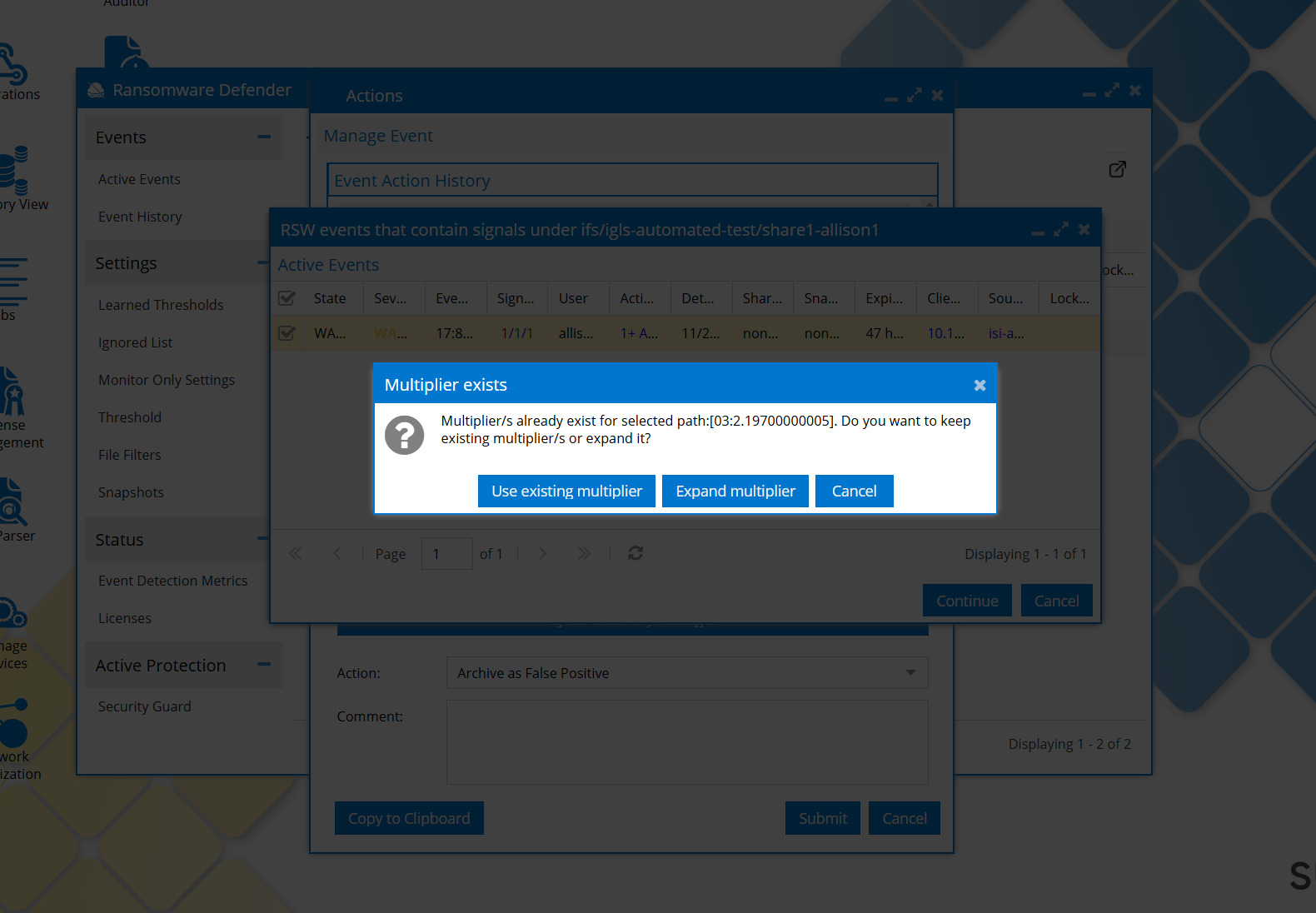
if we click Use Existing multiplier, the event is only archived, multiplier keeps its value.
If we click Expand multiplier => the multipliers are calculated as before (the old value of the multiplier is increased, new eventual multipliers are saved)
If, After choosing the path, there are other events that have signals raised under the same path, those events will be displayed, and we can choose them as well:
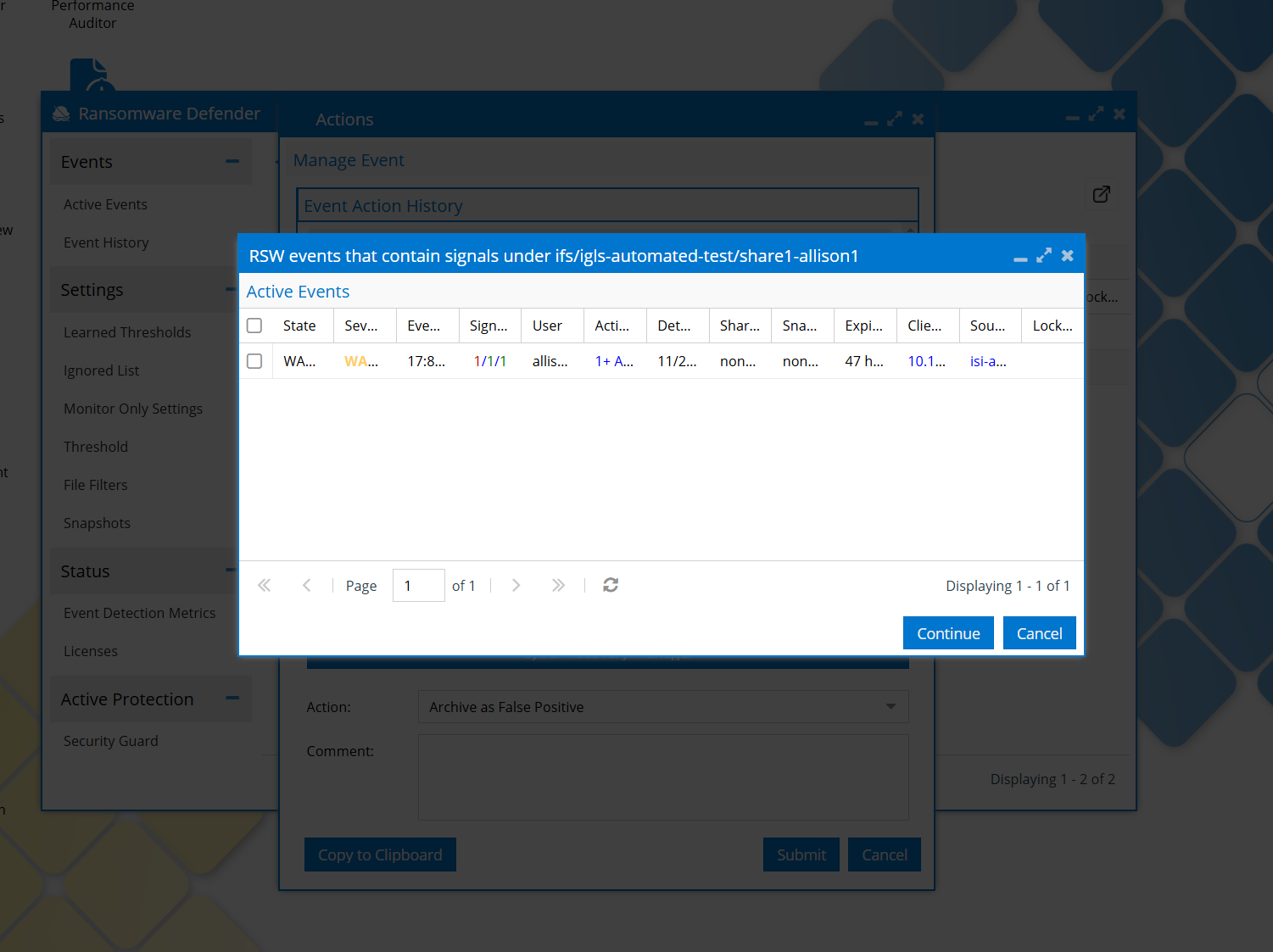
We can choose events from the list or we can choose none. On continue, the multiplier check above is done and displayed the confirmation window if there is already a multiplier.
Take note that on continue, if we selected some extra events from the displayed list, those events will only be archived, will not be taken into account in calculating new multipliers values. I considered that otherwise the multipliers can expand too much, with no control.
How to manually flag a security Event as False Positive
- Open the actions menu and select false-positive action and submit.
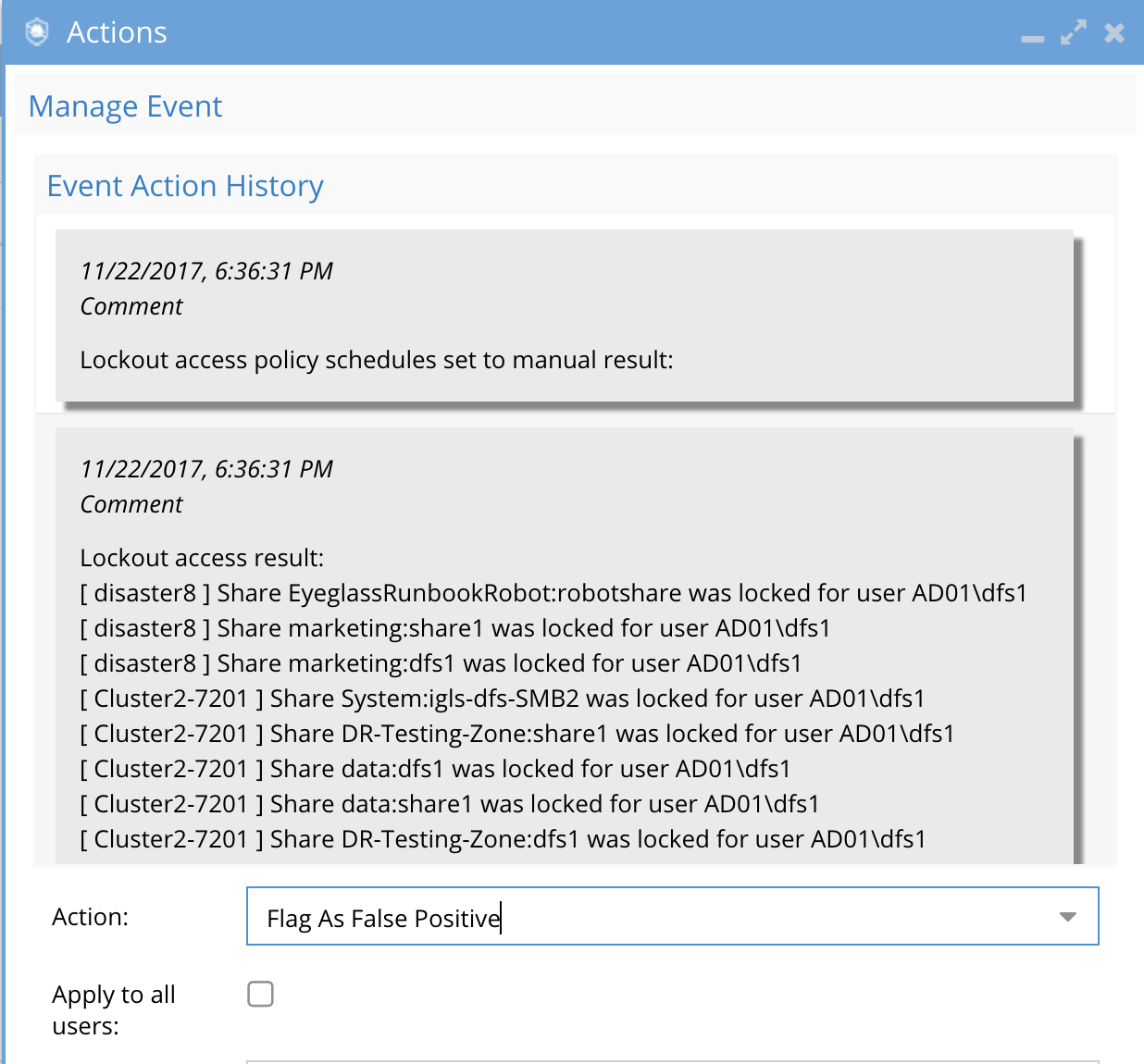
- This will update the settings for this user. This change is real-time and will take effect immediately.
- To view the settings for any custom user settings or flag as false-positive user settings click on the Learned Thresholds tab under the settings menu.
.png)
How to View or Delete a Flag as False Positive User setting
If you accidentally flagged as false positive or want to undo a user override setting. Follow these steps.
- Open the Ransomware Defender Icon
- Click on Settings-->Learnd Thresholds tab
- Find the user setting in the list and click the delete red X to remove this setting.
- NOTE: This change will take effect immediately and the ECA will be updated with the new settings for new events that are processed.
How to manually configure per-user Threat level settings with IGLS CLI
IGLS CLI commands exist to add and delete per user threat level override settings without waiting for a security event to teach.
Enter commands to create unique settings per user. This avoids the need for whitelisting users and can customize the settings per user. These settings are downloaded to the ECA cluster and processed in real-time once set as events flow through the cluster.
See Admin guide for complete documentation on the CLI commands
Global, Group-Specific and Selected Path Threshold Settings for False Positives
In addition to individual user settings, Ransomware Defender now supports the application of learned threshold settings globally or to specified user groups, or to a specific path. For this, the generic threshold feature must be enabled.
Enabling Generic Threshold Configuration
To activate the global threshold feature, administrators must use the Eyeglass CLI command:
igls rsw genericthresholds set --enabled=true
This command enables the feature, making it accessible within the user interface for further configuration.
Applying Thresholds
When flagging an event as a false positive, the interface offers four options for applying the new threshold settings: to the individual user, to a user group, globally across all users, or to a specific path.
Selecting the Current user option will update the settings for this user. This is the same case as the default behavior when genericthresholds was disabled:
Selecting the global (All users)threshold option, will present a warning to ensure the administrator is aware of the widespread impact of this action. This precaution helps prevent unintentional global changes:
With Selected Users Groups, the new threshold will apply to all the users in the selected groups
After saving the selected option, the new threshold settings will be visible under the "Learned Thresholds" tab:
Selected Path will allow us to select a path from a tree:
If the selected path has already a threshold associated, the user is asked whether to upgrade the multiplier or just archive the event: (Note that this behavior is only for the “Selected Path case”. For the other threshold types the multiplier is expanded automatically)
Also, if there are other active events that contain signals under the selected path, they are listed so the user can choose to archive them also or not :
Selected events will be archived, those not selected will remain active.
At the end, after the event is archived as false positive on a path, the selected path will be displayed in the same “Learned Thresholds” together with the user related thresholds: