- Overview
- Support Statement
- Capabilities
- Configuration Diagram
- Processes:
- Mapping Class
- Creating Customized CI Class Procedure
- CI Class Relationship View
- Integration Import Configuration
- ServiceNow CMDB
- CMDB CI Search
- CMDB Customized View
- Eyeglass Configuration
- Prerequisites
- XML to Excel format Conversion
- Attach Excel files to ServiceNow Data Sources
- Schedule jobs through Crontabs
Overview
ServiceNow CMDB integration allows cluster storage inventory to be synchronized into a custom CI schema to capture key properties of the cluster including hardware serial numbers, capacity, usage and SMB and NFS exports along with protection status and Quota usage. Customers can now fully leverage ServiceNow ITSM with NAS storage. Eyeglass collects the inventory of PowerScale Cluster and populates an XML file name servicenow.xml. In this document we use that XML file as the input for importing into ServiceNow CMDB.
Support Statement
- NOTE: This documentation is provided "as is" without support for 3rd party software. The level of support for this integration guide is best effort without any SLA on response time. No 3rd party product support can be provided by Superna directly. 3rd party components require support contracts
Capabilities
- This integration enables customers to create incidents against shares and exports
- Monitor cluster storage capacity and usage within ServiceNow
- Manage Maintenance windows to calculator business impacted services
- Link services and applications to IT resources based on dependencies to file storage
- Fully integrate cluster NAS storage into ITSM workflows with ServiceNow
Configuration Diagram
The diagram below shows the setup
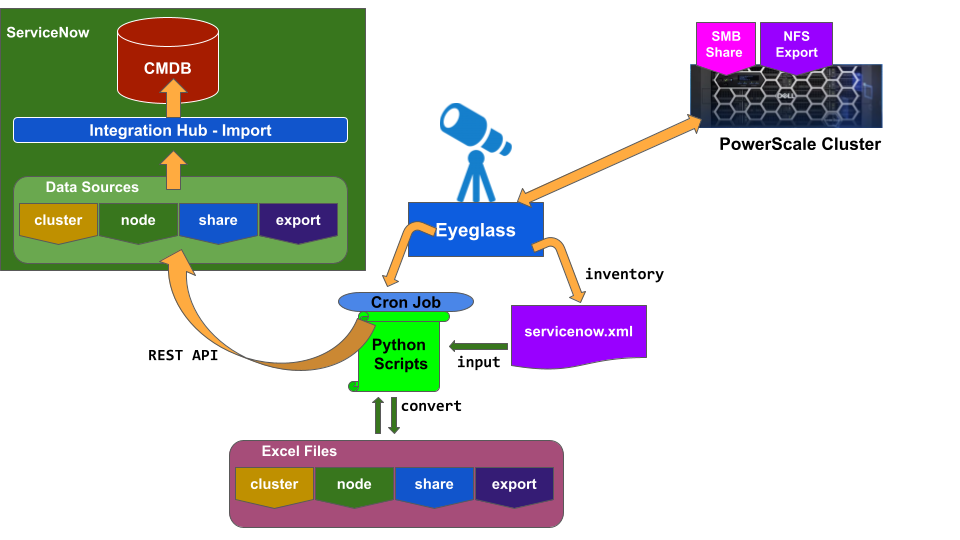
Processes:
- Eyeglass collects PowerScale Cluster Inventory and populates servicenow.xml file
- Through the scheduler set in Eyeglass crontab, python scripts will perform the following:
- Convert servicenow.xml into 4 Excel files:
- Excel file for Cluster
- Excel file for Node
- Excel file for SMB Share
- Excel file for NFS Export
- By using REST API, the script will attach those Excel Files to ServiceNow Data Sources
- Convert servicenow.xml into 4 Excel files:
- ServiceNow Integration Hub - Imports
- Schedule to automatically import from Data Sources
- Transform and Map to Customized Classes and populate the CMDB
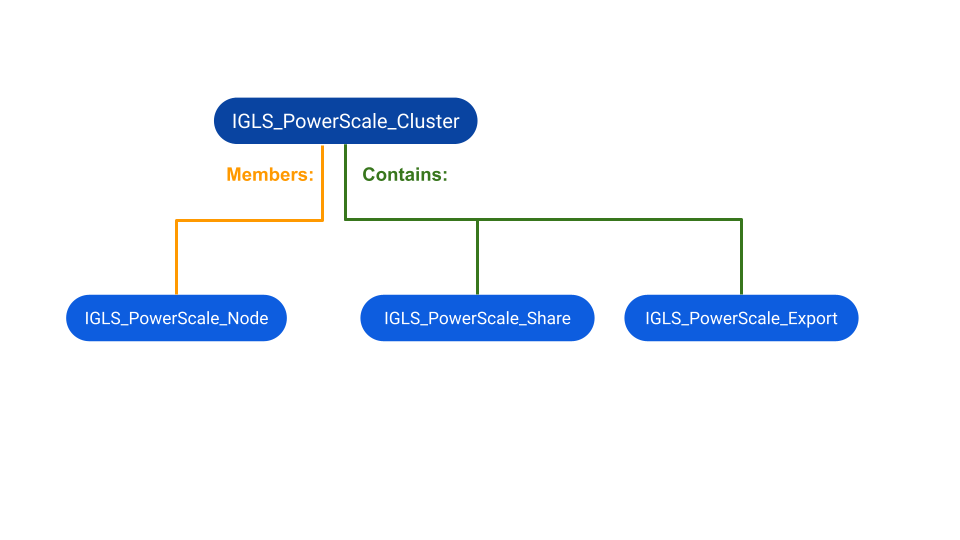
Mapping Class
For this integration we are creating new customized CI Classes with the following structures:
- Parent Class: IGLS_PowerScale_Cluster
- Child Class-1: IGLS_PowerScale_Node (Member of - relationship to IGLS_PowerScale_Cluster)
- Child Class-2: IGLS_PowerScale_Share (Contained by - relationship to IGLS_PowerScale_Cluster)
- Child Class-3: IGLS_PowerScale_Export (Contained by - relationship to IGLS_PowerScale_Cluster)
Creating Customized CI Class Procedure
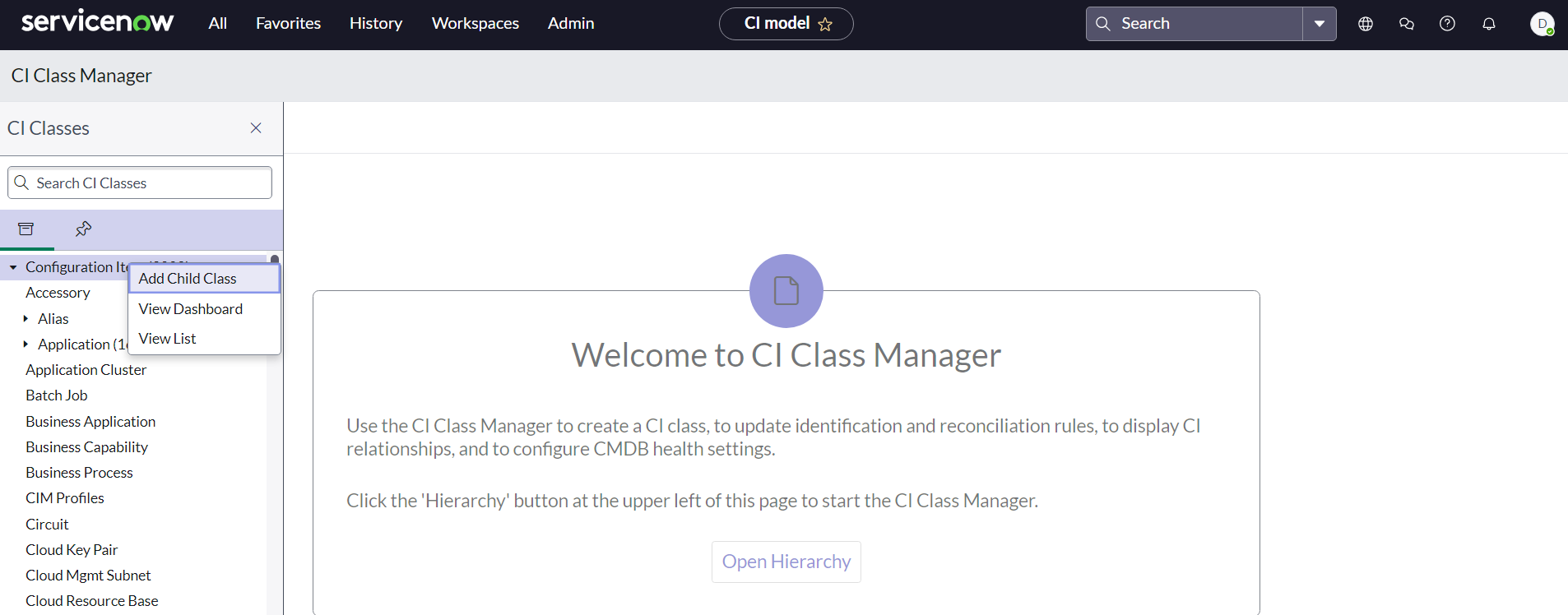
- Open CI Class Manager
- Click Hierarchy to expand the CI Classes list. Then select the class that the new class is extended from.
- For the new Parent Class IGLS_PowerScale_Cluster, we create as a new Class directly under the top Configuration Item Parent Folder Structure
- For the new Children Classes (IGLS_PowerScale_Node, IGLS_PowerScale_Share, IGLS_PowerScale_Export), we create as new Classes under the new Parent Class IGLS_PowerScale_Cluster
- To create a new class, select the parent class (refer to point 2a and 2b) , right click and select Add Child Class.
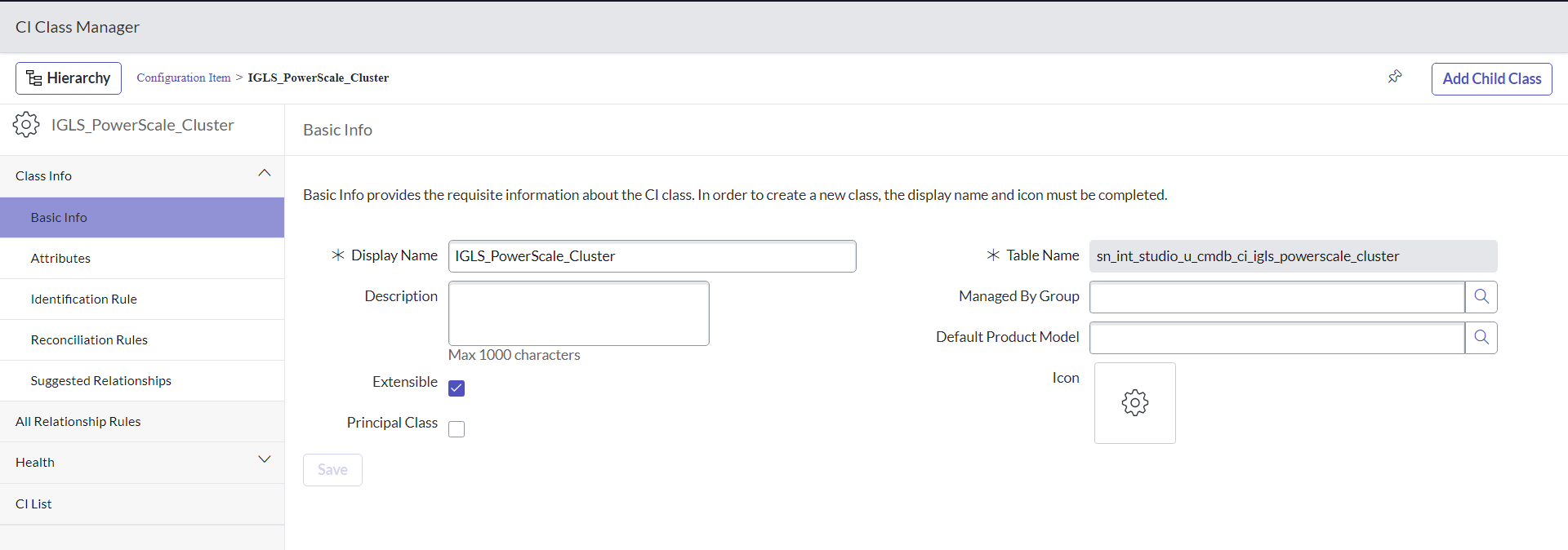
- The Add Child Class option appears only if the selected class is extendable. On the Provide Basic Info tab, fill out the information and then click Next
- Description of the fields:
| Field | Description |
| Display name |
|
| Table name | Automatically populated based on the table label and the prefix string 'u_cmdb_ci'. You cannot modify the prefix; however, you can modify the rest of the table name. The name can contain only lowercase, alphanumeric ASCII characters and underscores (_). Maximum string length is 80 characters. |
| Description | Explanation of the purpose of the class. |
| Icon | The icon associated with the class. |
| Extensible |
|
| Principal Class | Denotes whether this class is included in the Principal Class filter. If this class is included in the Principal Class filter, then CIs from this class appear in CI list views when the Principal Class filter is applied. This is optional. |
- Example:
- After we click the Next button, we can accept all the default options for the remaining configuration until it completes the creation of the new CI Class.
- Once the new CI Class is created, we can edit to modify the setting. For the Parent Class IGLS_PowerScale_Cluster, we need to add additional attributes.
- On the Add Attributes tab, click the + sign and enter details for each new class column. Then click Next.
Notes: We only need to add the following Attributes for the Parent Class IGLS_PowerScale Class (for the Children Classes we will use the inherited attributes from Parent Class:
| Attributes | Types | Description |
| Cluster_Name | String | PowerScale Cluster Name |
| Cluster_GUID | String | PowerScale Cluster GUID |
| Cluster_LocalSerial | String | PowerScale Cluster Local Serial Number |
| Cluster_OFSv_Build | String | PowerScale Cluster OneFS version Build |
| Cluster_OFSv_Release | String | PowerScale Cluster OneFS version Release |
| Cluster_OFSv_Type | String | PowerScale Cluster OneFS version Type |
| Cluster_OFSv_Version | String | PowerScale Cluster OneFS version Version |
| Cluster_OFSv_Revision | Integer | PowerScale Cluster OneFS version Revision |
| Node_Health | String | PowerScale Node Health |
| Node_SerialNumber | String | PowerScale Node Serial Number |
| Node_HDDsize | String | PowerScale Node HDD Size |
| Node_HDDused | String | PowerScale Node HDD Used |
| Node_HDDavail | String | PowerScale Node HDD Avail |
| Share_Name | String | PowerScale Share Name |
| Share_Path | String | PowerScale Share Path |
| Share_Zone | String | PowerScale Share Zone |
| Share_Status | String | PowerScale Share Status |
| Export_Paths | String | PowerScale Export Paths |
| Export_Zone | String | PowerScale Export Zone |
| Export_Status | String | PowerScale Export Status |
- For the Children Classes, we set the Relationship as follows in the Suggested Relationship section:
Child | Child Relationship to Parent | Parent | Parent Relationship to Child |
IGLS_PowerScale_Node | Member of: | IGLS_PowerScale_Cluster | Member: |
| IGLS_PowerScale_Share | Contained by: | IGLS_PowerScale_Cluster | Contain: |
| IGLS_PowerScale_Export | Contained by: | IGLS_PowerScale_Cluster | Contain: |
Example:
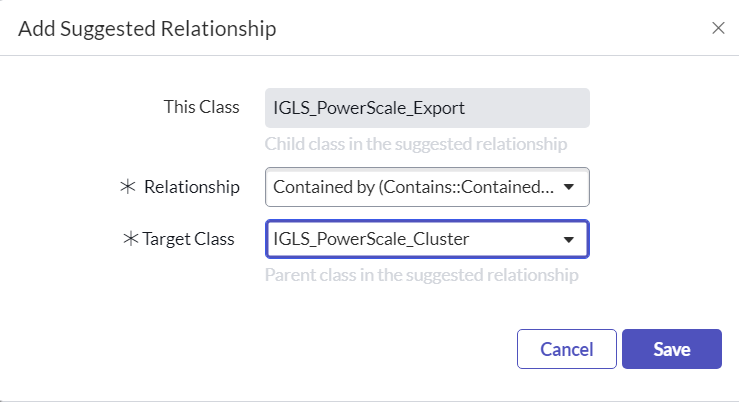
- Once we have completed the creation of all those 4 CI Classes, then we configure Integration Import Jobs
CI Class Relationship View
To view CI Class Relationship View between Parent and Children, we can click the Suggested Relationships menu from the Parent CI Class
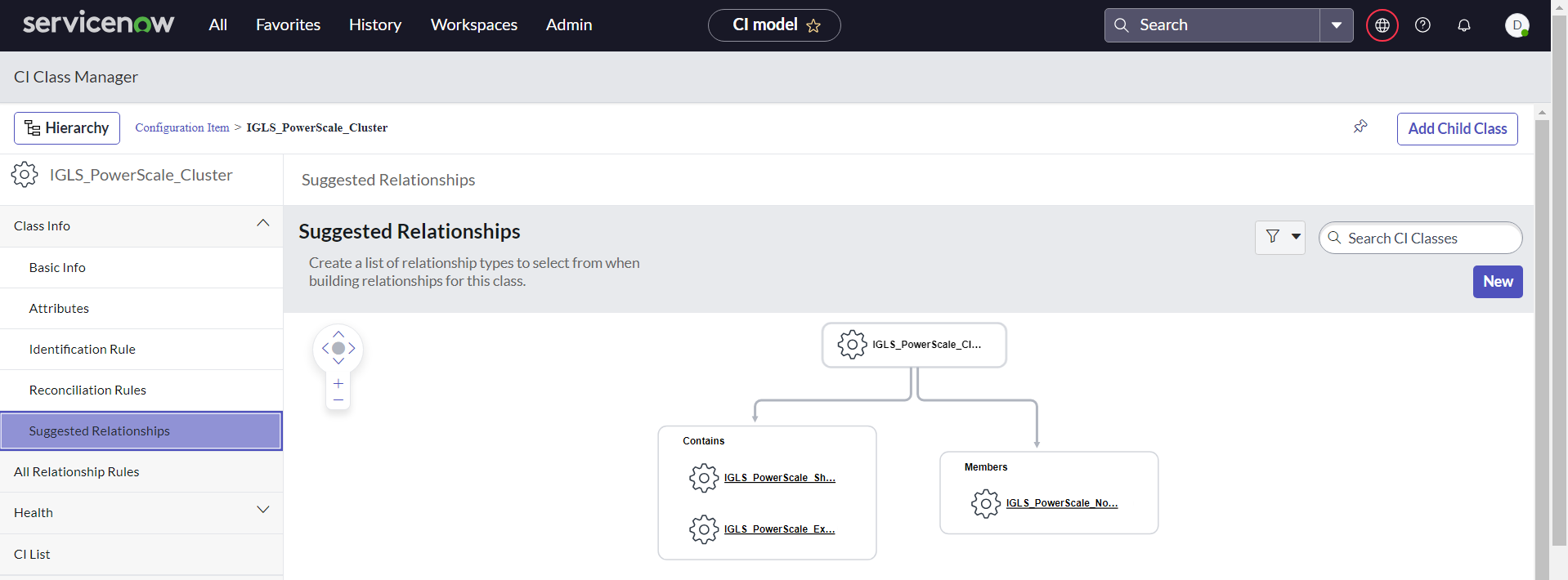
Integration Import Configuration
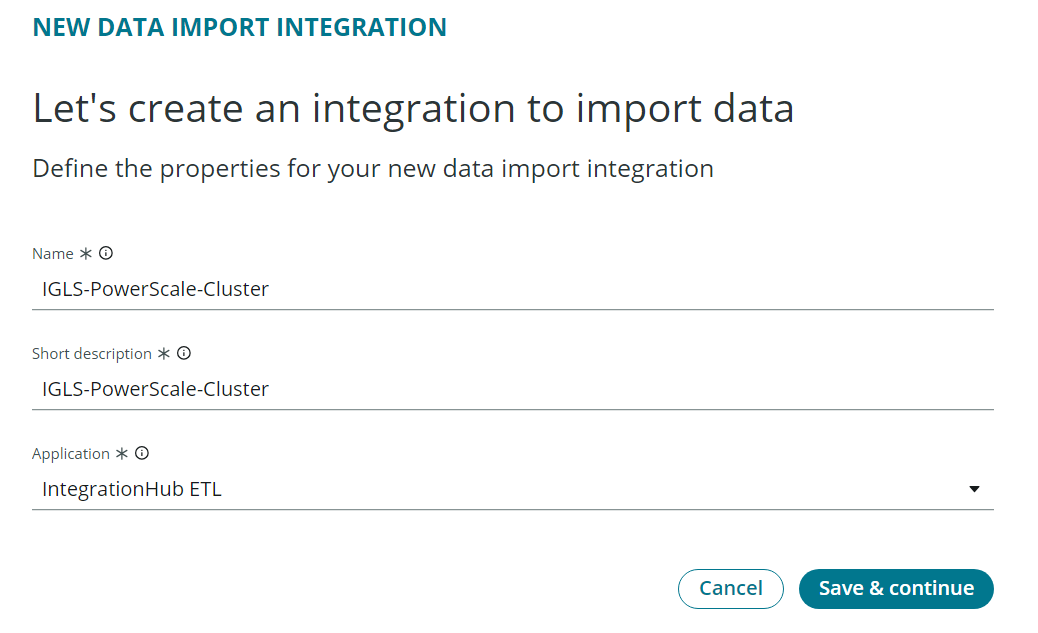
- Open IntegrationHub - Import tool
- Specify the name of the Integration Data Import and provide the Short Description.
- We need to create 4 Integration Import jobs:
| Integration Import Name | |
| 1 | IGLS-PowerScale-Cluster |
| 2 | IGLS-PowerScale-Node |
| 3 | IGLS-PowerScale-Share |
| 4 | IGLS-PowerScale-Export |
- Example
- Specify the Source Type ⇒ Excel File
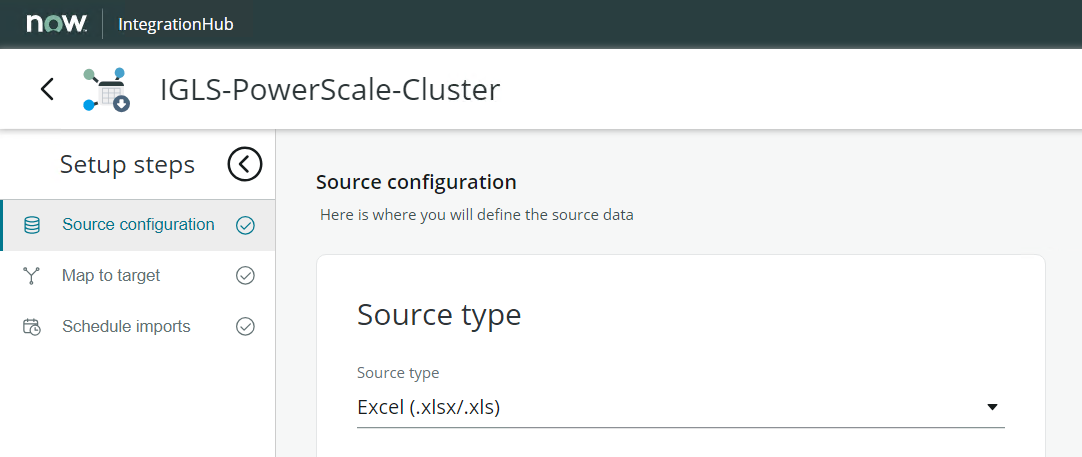
- Select and Upload the initial Excel File manually
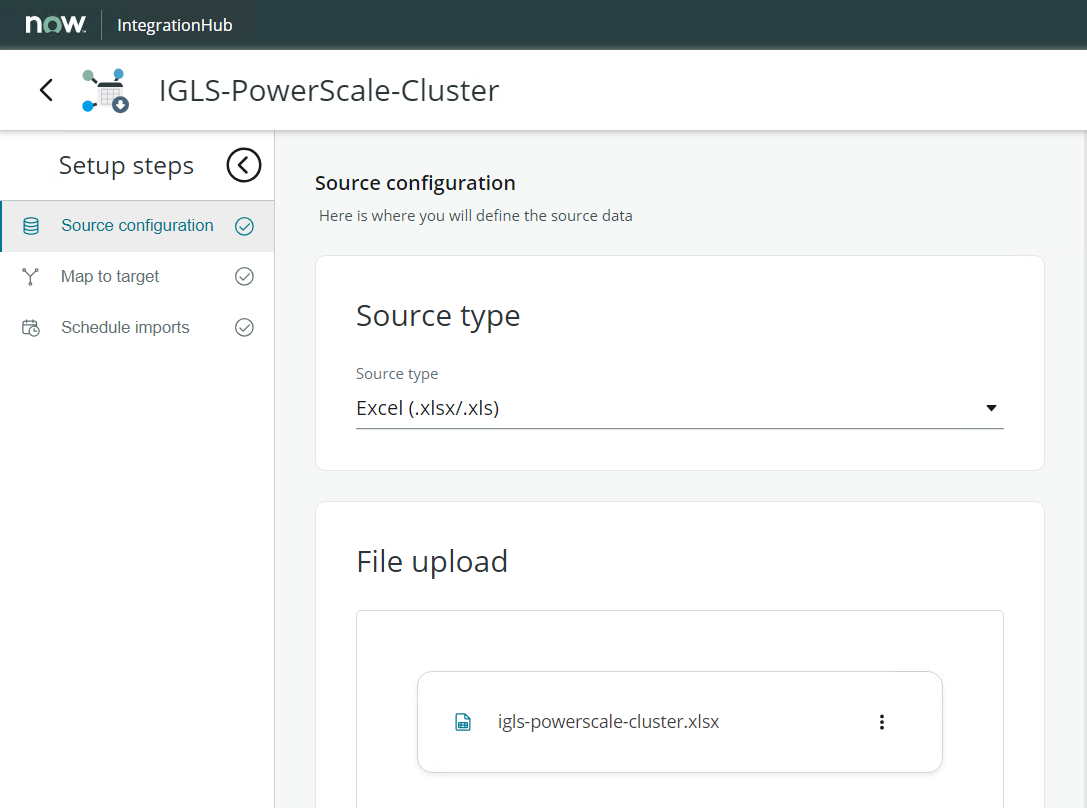
- Next step is to configure the mapping. In the Map to Target tab, click Add a Mapping Button
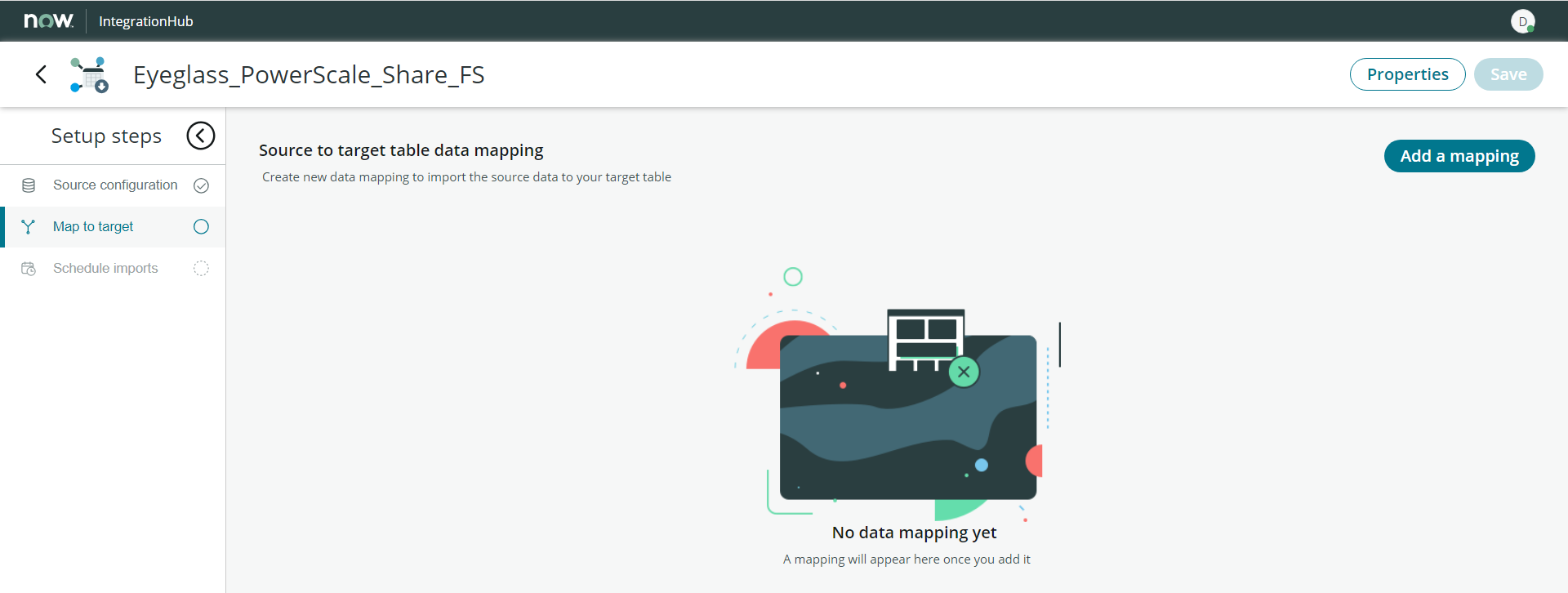
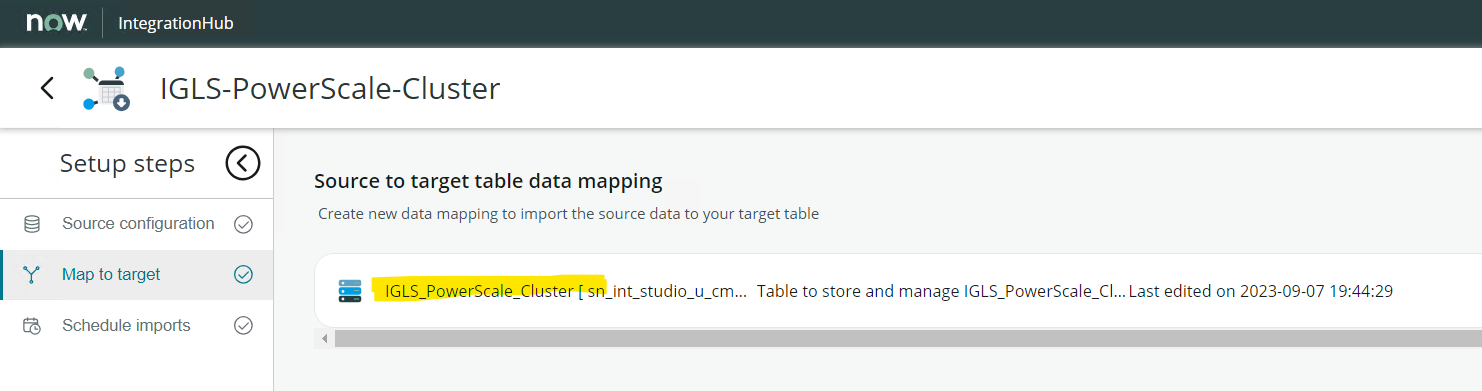
- Select the newly created Class as the target for this mapping
Integration Import Name | Mapping Target Class |
IGLS-PowerScale-Cluster | IGLS_PowerScale_Cluster |
| IGLS-PowerScale-Node | IGLS_PowerScale_Node |
| IGLS-PowerScale-Share | IGLS_PowerScale_Share |
| IGLS-PowerScale-Export | IGLS_PowerScale_Export |
- Click the Target table data mapping name from this UI to open the Mapping Configuration window
- Configure the Mapping and Save the mapping configuration
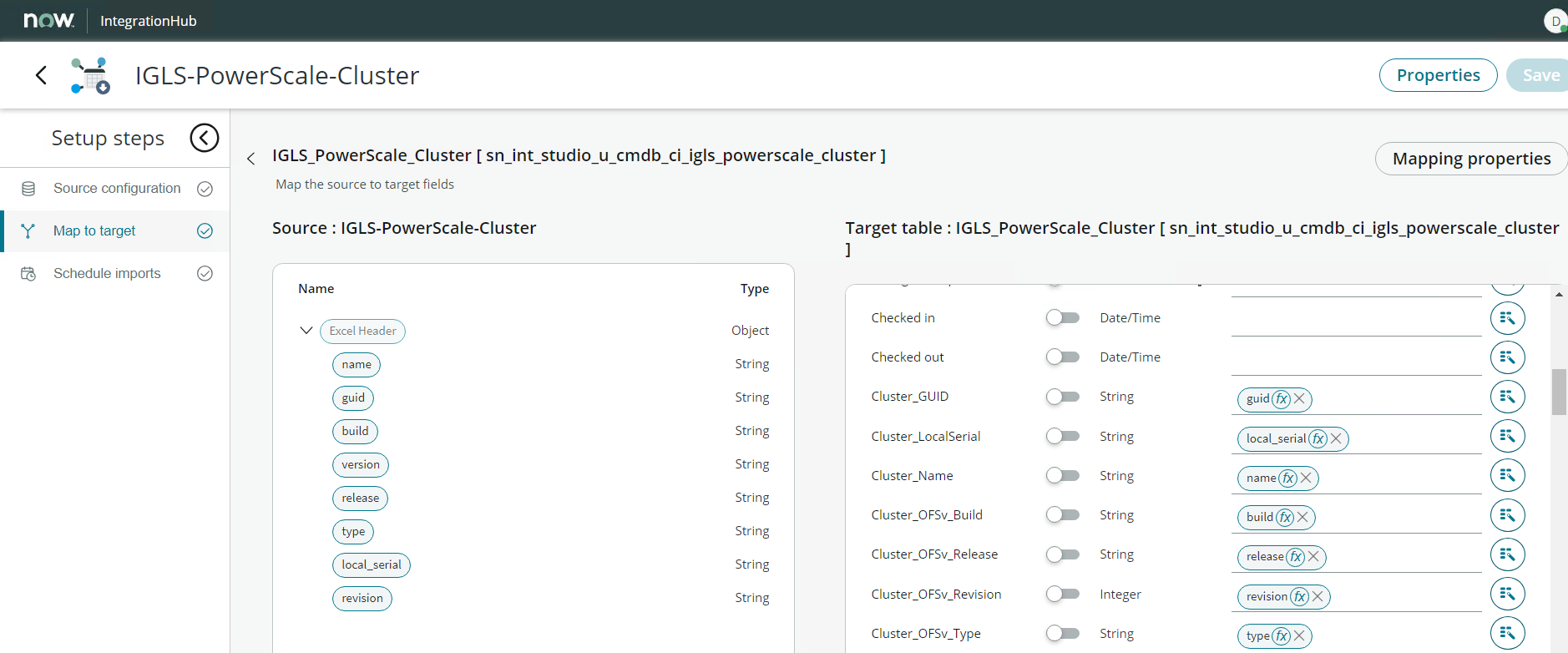
Mapping:
Integration Import: IGLS-PowerScale-Cluster
| Target | Match (Enable / Disable)* | Source |
| name | Enable | name |
| Cluster_Name | Disable (Default) | name |
| Cluster_GUID | Disable (Default) | guid |
| Cluster_LocalSerial | Disable (Default) | local_serial |
| Cluster_OFSv_Build | Disable (Default) | build |
| Cluster_OFSv_Release | Disable (Default) | release |
| Cluster_OFSv_Type | Disable (Default) | type |
| Cluster_OFSv_Version | Disable (Default) | version |
| Cluster_OFSv_Revision | Disable (Default) | revision |
Integration Import: IGLS-PowerScale-Node
| Target | Match (Enable / Disable)* | Source |
| name | Enable | name\serial_number |
| Cluster_Name | Disable (Default) | name |
| Cluster_GUID | Disable (Default) | guid |
| Node_Health | Disable (Default) | health |
| Node_SerialNumber | Disable (Default) | serial_number |
| Node_HDDsize | Disable (Default) | HDD_size |
| Node_HDDused | Disable (Default) | HDD_used |
| Node_HDDavail | Disable (Default) | HDD_avail |
Integration Import: IGLS-PowerScale-Share
| Target | Match (Enable / Disable)* | Source |
| name | Enable | name\zone\name2 |
| Cluster_Name | Disable (Default) | name |
| Cluster_GUID | Disable (Default) | guid |
| Share_Name | Disable (Default) | name2 |
| Share_Path | Disable (Default) | path |
| Share_Zone | Disable (Default) | zone |
| Share_Status | Disable (Default) | status |
Integration Import: IGLS-PowerScale-Export
| Target | Match (Enable / Disable)* | Source |
| name | Enable | name\zone3\paths |
| Cluster_Name | Disable (Default) | name |
| Cluster_GUID | Disable (Default) | guid |
| Export_Paths | paths | paths |
| Export_Zone | zone3 | zone3 |
| Export_Status | status4 | status4 |
*Match Toggle Switch:
Toggle switch to specify fields where the system should check for matching data and, if found, update existing records instead of creating new ones.
Once completed, click the Save button to save the configuration.
- Set Import Schedule
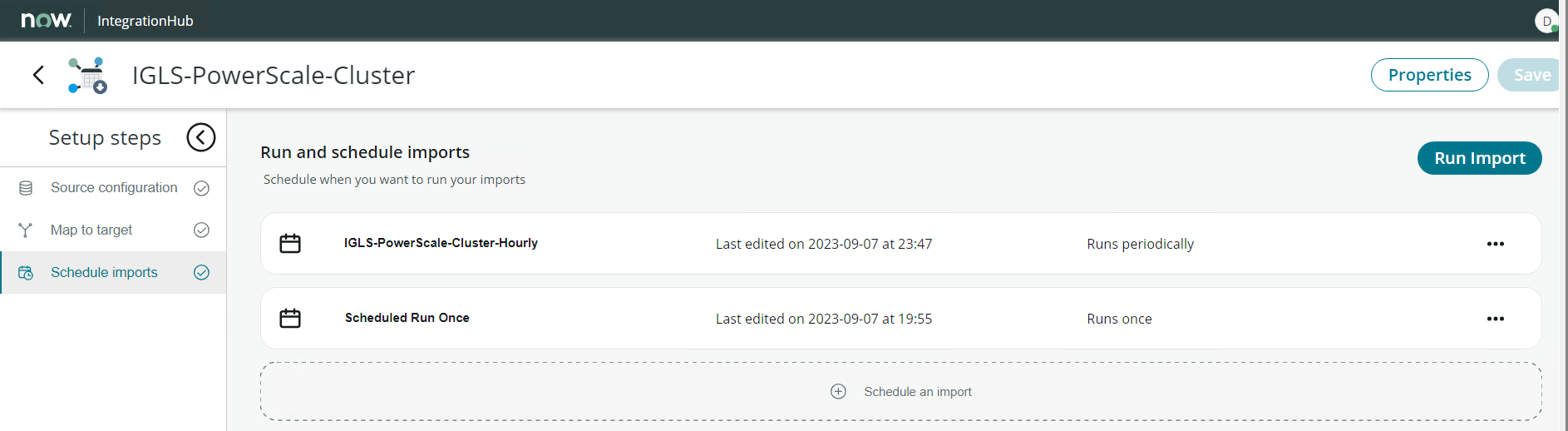
Example: run periodically - every hour

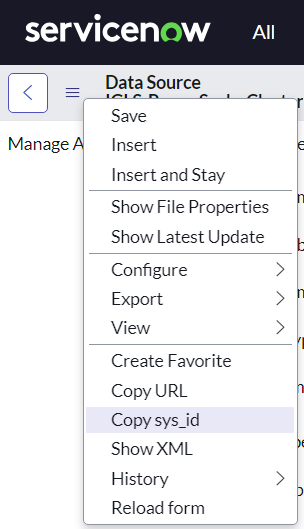
Data Source Table Name and Table Sys ID
For each ServiceNow Data Source we need to get the Table Sys ID for attaching the Excel file into the corresponding Data Source.
To get the Table Sys ID, we can copy that sys id from Data Source Menu and then select => Copy sys id
ServiceNow CMDB
CMDB CI Search
For searching CIs from ServiceNow CMDB:
- Switch to the CMDB Workspace view
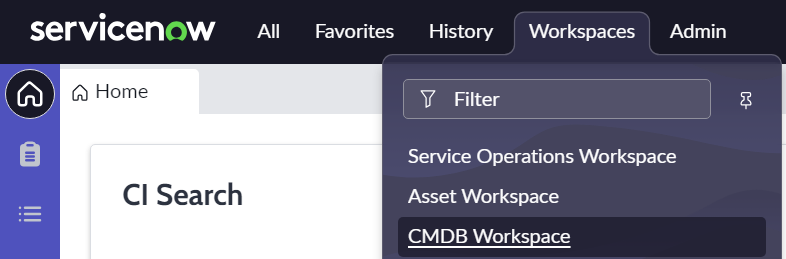
- Specify CI Search Criteria and click the Search button
- Class
- Field
- Operator
- Value
- Example:
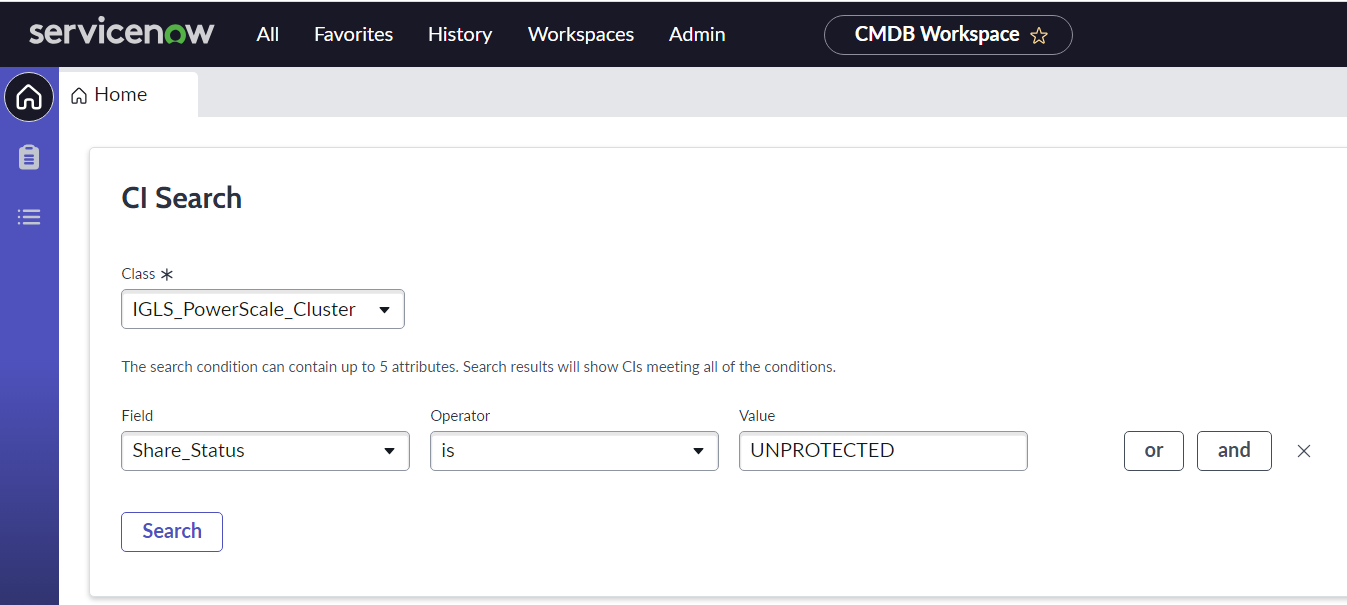
- Example of CI Search result:
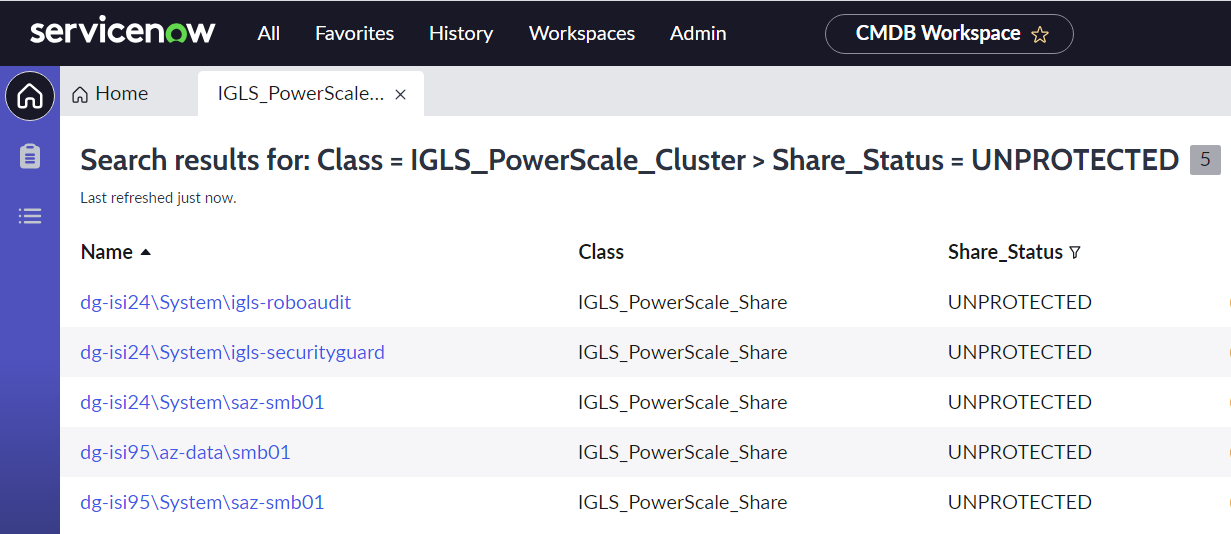
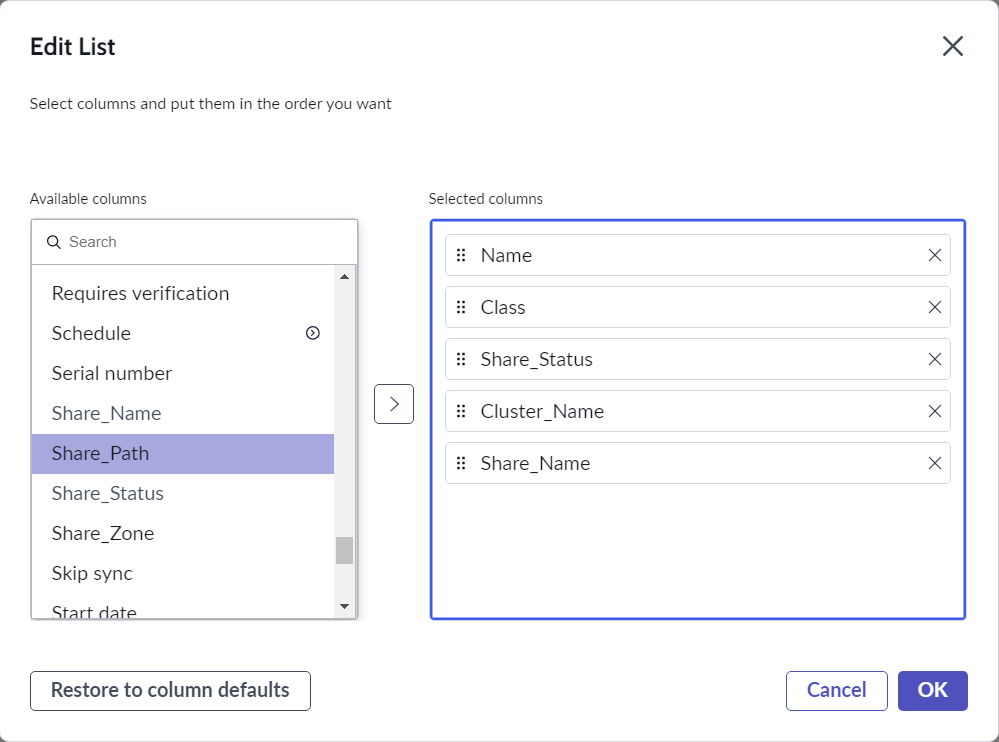
- We can customize the column view of the result. Click Edit Columns button from the menu

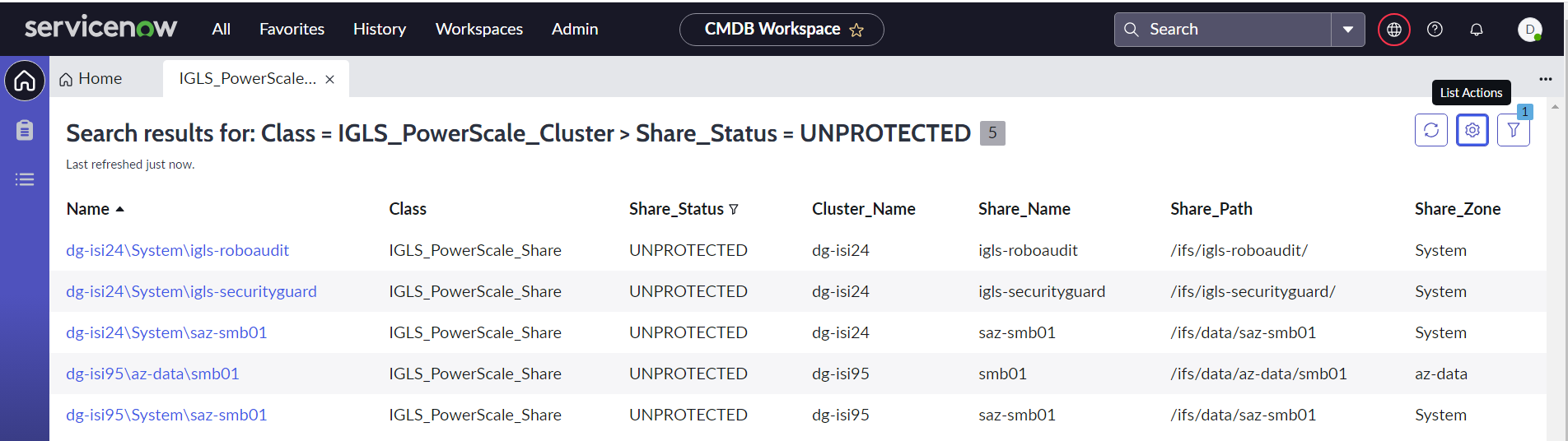
- Select columns to view, and then click the OK button
- Example:
CMDB Customized View
For setting CMDB Customized View:
- Switch to the CMDB Workspace view

- Click the List button from the left hand side of the CMDB menu, and click My Lists tab
- Click Add New List button at the bottom of the CMDB workspace

- We can create a new list from existing or create our own. Example for creating a new list based on our own settings. Specify List Name, Source (CMDB table) , Columns. Then click Create button.

- We can see our list result. Example:
Eyeglass Configuration
Prerequisites
- Configure servicenow output directory
- login to eyeglass VM
- mv /srv/www/htdocs/{servicenow} /srv/www/htdocs/servicenow
- Install additional python modules
- login as eyeglass admin user
- pip install pandas
- pip install openpyxl
The following components are configured in Eyeglass
- XML to Excel format Conversion
- Attach Excel files to ServiceNow Data Sources
- Schedule jobs through Crontabs
XML to Excel format Conversion
We need to convert the servicenow.xml file into 4 Excel files:
- Excel file for Cluster
- Excel file for Node
- Excel file for SMB Share
- Excel file for NFS Export
We use the following python scripts to perform that tasks:
Python Scripts | Task |
igls-convert-cluster.py | Convert servicenow.xml ⇒ igls-powerscale-cluster.xlsx |
igls-convert-node.py | Convert servicenow.xml ⇒ igls-powerscale-node.xlsx |
igls-convert-share.py | Convert servicenow.xml ⇒ igls-powerscale-share.xlsx |
igls-convert-export.py | Convert servicenow.xml ⇒ igls-powerscale-export.xlsx |
We place those python scripts in /home/admin directory and will be run as admin user
igls-convert-cluster.py
===============
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pandas as pd
# Define the file path for the XML data
xml_file_path = '/srv/www/htdocs/servicenow/servicenow.xml' # Replace with the actual file path
# Parse the XML data from the file
tree = ET.parse(xml_file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
# Initialize lists to store data
clusters = []
# Extract data from XML
for element in root.findall('.//element'):
cluster_name = element.find('.//cluster/name').text
cluster_guid = element.find('.//cluster/guid').text
cluster_local_serial = element.find('.//cluster/local_serial').text
cluster_type = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/type').text
cluster_release = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/release').text
cluster_build = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/build').text
cluster_version = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/version').text
cluster_revision = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/revision').text
clusters.append([cluster_name, cluster_guid, cluster_local_serial, cluster_type, cluster_release, cluster_build, cluster_version, cluster_revision])
# Create a DataFrame from the extracted data
df = pd.DataFrame(clusters, columns=['name', 'guid', 'local_serial', 'type', 'release', 'build', 'version', 'revision'])
# Save the DataFrame to an Excel file
output_file = '/home/admin/igls-powerscale-cluster.xlsx'
df.to_excel(output_file, index=False)
print(f'Data saved to {output_file}')
==============
igls-convert-node.py
========================
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pandas as pd
# Define the file path for the XML data
xml_file_path = '/srv/www/htdocs/servicenow/servicenow.xml' # Replace with the actual file path
# Parse the XML data from the file
tree = ET.parse(xml_file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
# Initialize lists to store data
clusters = []
nodes = []
# Extract data from XML
for element in root.findall('.//element'):
cluster_name = element.find('.//cluster/name').text
cluster_guid = element.find('.//cluster/guid').text
cluster_local_serial = element.find('.//cluster/local_serial').text
cluster_type = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/type').text
cluster_release = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/release').text
cluster_build = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/build').text
cluster_version = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/version').text
cluster_revision = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/revision').text
node_elements = element.findall('.//nodes/node')
for node_element in node_elements:
node_serialnumber = node_element.find('serial_number').text
node_health = node_element.find('health').text
node_hddsize = node_element.find('HDD_size').text
node_hddused = node_element.find('HDD_used').text
node_hddavail = node_element.find('HDD_avail').text
nodes.append([cluster_name, cluster_guid, node_serialnumber, node_health, node_hddsize, node_hddused, node_hddavail])
# Create a DataFrame from the extracted data
df = pd.DataFrame(nodes, columns=['name', 'guid', 'serial_number', 'health', 'HDD_size', 'HDD_used', 'HDD_avail'])
# Save the DataFrame to an Excel file
output_file = '/home/admin/igls-powerscale-node.xlsx'
df.to_excel(output_file, index=False)
print(f'Data saved to {output_file}')
========================
igls-convert-share.py
===================
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pandas as pd
# Define the file path for the XML data
xml_file_path = '/srv/www/htdocs/servicenow/servicenow.xml' # Replace with the actual file path
# Parse the XML data from the file
tree = ET.parse(xml_file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
# Initialize lists to store data
clusters = []
shares = []
# Extract data from XML
for element in root.findall('.//element'):
cluster_name = element.find('.//cluster/name').text
cluster_guid = element.find('.//cluster/guid').text
cluster_local_serial = element.find('.//cluster/local_serial').text
cluster_type = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/type').text
cluster_release = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/release').text
cluster_build = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/build').text
cluster_version = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/version').text
cluster_revision = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/revision').text
share_elements = element.findall('.//shares/share')
for share_element in share_elements:
share_name = share_element.find('name').text
share_status = share_element.find('status').text
share_path = share_element.find('path').text
share_zone = share_element.find('zone').text
shares.append([cluster_name, cluster_guid, cluster_type, share_name, share_status, share_path, share_zone])
# Create a DataFrame from the extracted data
df = pd.DataFrame(shares, columns=['name', 'guid', 'type', 'name2', 'status', 'path', 'zone'])
# Save the DataFrame to an Excel file
output_file = '/home/admin/igls-powerscale-share.xlsx'
df.to_excel(output_file, index=False)
print(f'Data saved to {output_file}')
===================
igls-convert-export.py
===================
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pandas as pd
# Define the file path for the XML data
xml_file_path = '/srv/www/htdocs/servicenow/servicenow.xml' # Replace with the actual file path
# Parse the XML data from the file
tree = ET.parse(xml_file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
# Initialize lists to store data
clusters = []
exports = []
# Extract data from XML
for element in root.findall('.//element'):
cluster_name = element.find('.//cluster/name').text
cluster_guid = element.find('.//cluster/guid').text
cluster_local_serial = element.find('.//cluster/local_serial').text
cluster_type = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/type').text
cluster_release = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/release').text
cluster_build = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/build').text
cluster_version = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/version').text
cluster_revision = element.find('.//cluster/onefs_version/revision').text
export_elements = element.findall('.//exports/export')
for export_element in export_elements:
export_paths = export_element.find('paths').text
export_status = export_element.find('status').text
export_zone = export_element.find('zone').text
exports.append([cluster_name, cluster_guid, cluster_type, export_paths, export_status, export_zone])
# Create a DataFrame from the extracted data
df = pd.DataFrame(exports, columns=['name', 'guid', 'type', 'paths', 'status3', 'zone4'])
# Save the DataFrame to an Excel file
output_file = '/home/admin/igls-powerscale-export.xlsx'
df.to_excel(output_file, index=False)
print(f'Data saved to {output_file}')
===================
Attach Excel files to ServiceNow Data Sources
Once the Excel files are generated, the next step is to attach those files to ServiceNow Data Sources by using the REST API (attachment) commands.
We use the following python scripts to perform that tasks:
| Python Scripts | Task |
| igls-snapi-cluster.py | Attach the igls-powerscale-cluster.xlsx to ServiceNow IGLS-PowerScale-Cluster Data Source |
| igls-snapi-node.py | Attach the igls-powerscale-node.xlsx to ServiceNow IGLS-PowerScale-Node Data Source |
| igls-snapi-share.py | Attach the igls-powerscale-share.xlsx to ServiceNow IGLS-PowerScale-Share Data Source |
| igls-snapi-export.py | Attach the igls-powerscale-export.xlsx to ServiceNow IGLS-PowerScale-Export Data Source |
We place those python scripts in /home/admin directory and will be run as admin user.
igls-snapi-cluster.py
=========
import requests
# Replace these with your own ServiceNow instance details and credentials
instance_url = "https://<servicenow-instance-name>.service-now.com" # Specify ServiceNow instance URL
username = "<servicenow-user-api>" # specify user to execute this api
password = "<servicenow-password-api>" # specify user password to execute this api
# Set the URL for the ServiceNow REST API
rest_api_url = f"{instance_url}/api/now/attachment"
# Specify the table and table_sys_id where you want to attach the file
table_name = "sys_data_source" # Replace with the target table name
table_sys_id = "<specify-target-table-sys-id>" # Replace with the target table sys_id
# Specify the file you want to attach
file_name = "igls-powerscale-cluster.xlsx"
file_path = f"/home/admin/{file_name}"
# Create a session for making authenticated requests
session = requests.Session()
session.auth = (username, password)
# Set proper headers
headers = {"Content-Type":"application/json","Accept":"application/json"}
# Set sysparm_limit
sysparm_query = f"file_name={file_name}"
# Check if an existing attachment exists and delete it
check_url = f'{rest_api_url}?sysparm_limit=2&sysparm_query={sysparm_query}'
existing_attachment_response = session.get(check_url, headers=headers)
if existing_attachment_response.status_code == 200:
existing_attachments = existing_attachment_response.json().get("result")
# Delete existing attachments
for attachment in existing_attachments:
if attachment.get("table_sys_id") == table_sys_id:
sys_id = attachment.get("sys_id")
delete_attachment_url = f"{rest_api_url}/{sys_id}"
delete_response = session.delete(delete_attachment_url)
if delete_response.status_code == 204:
print(f"Existing attachment with sys_id {sys_id} deleted.")
else:
print(f"Failed to delete existing attachment with sys_id {sys_id}. Status code: {delete_response.status_code}")
else:
print(f"Failed to check for existing attachment. Status code: {existing_attachment_response.status_code}")
print(existing_attachment_response.text)
# Send a POST request to upload the new file
new_attachment_url = f"{rest_api_url}/file?table_name={table_name}&table_sys_id={table_sys_id}&file_name={file_name}"
data = open(f'{file_path}', 'rb').read()
response = session.post(new_attachment_url, headers=headers, data=data)
# Check if the request was successful
if response.status_code == 201:
attachment_info = response.json().get("result")
sys_id = attachment_info.get("sys_id")
print(f"Attachment uploaded successfully. sys_id: {sys_id}")
else:
print(f"Failed to upload attachment. Status code: {response.status_code}")
print(response.text)
=========
igls-snapi-node.py
=========
import requests
# Replace these with your own ServiceNow instance details and credentials
instance_url = "https://<servicenow-instance-name>.service-now.com" # Specify ServiceNow instance URL
username = "<servicenow-user-api>" # specify user to execute this api
password = "<servicenow-password-api>" # specify user password to execute this api
# Set the URL for the ServiceNow REST API
rest_api_url = f"{instance_url}/api/now/attachment"
# Specify the table and table_sys_id where you want to attach the file
table_name = "sys_data_source" # Replace with the target table name
table_sys_id = "<specify-target-table-sys-id>" # Replace with the target table sys_id
# Specify the file you want to attach
file_name = "igls-powerscale-node.xlsx"
file_path = f"/home/admin/{file_name}"
# Create a session for making authenticated requests
session = requests.Session()
session.auth = (username, password)
# Set proper headers
headers = {"Content-Type":"application/json","Accept":"application/json"}
# Set sysparm_limit
sysparm_query = f"file_name={file_name}"
# Check if an existing attachment exists and delete it
check_url = f'{rest_api_url}?sysparm_limit=2&sysparm_query={sysparm_query}'
existing_attachment_response = session.get(check_url, headers=headers)
if existing_attachment_response.status_code == 200:
existing_attachments = existing_attachment_response.json().get("result")
# Delete existing attachments
for attachment in existing_attachments:
if attachment.get("table_sys_id") == table_sys_id:
sys_id = attachment.get("sys_id")
delete_attachment_url = f"{rest_api_url}/{sys_id}"
delete_response = session.delete(delete_attachment_url)
if delete_response.status_code == 204:
print(f"Existing attachment with sys_id {sys_id} deleted.")
else:
print(f"Failed to delete existing attachment with sys_id {sys_id}. Status code: {delete_response.status_code}")
else:
print(f"Failed to check for existing attachment. Status code: {existing_attachment_response.status_code}")
print(existing_attachment_response.text)
# Send a POST request to upload the new file
new_attachment_url = f"{rest_api_url}/file?table_name={table_name}&table_sys_id={table_sys_id}&file_name={file_name}"
data = open(f'{file_path}', 'rb').read()
response = session.post(new_attachment_url, headers=headers, data=data)
# Check if the request was successful
if response.status_code == 201:
attachment_info = response.json().get("result")
sys_id = attachment_info.get("sys_id")
print(f"Attachment uploaded successfully. sys_id: {sys_id}")
else:
print(f"Failed to upload attachment. Status code: {response.status_code}")
print(response.text)
=========
igls-snapi-share.py
========
import requests
# Replace these with your own ServiceNow instance details and credentials
instance_url = "https://<servicenow-instance-name>.service-now.com" # Specify ServiceNow instance URL
username = "<servicenow-user-api>" # specify user to execute this api
password = "<servicenow-password-api>" # specify user password to execute this api
# Set the URL for the ServiceNow REST API
rest_api_url = f"{instance_url}/api/now/attachment"
# Specify the table and table_sys_id where you want to attach the file
table_name = "sys_data_source" # Replace with the target table name
table_sys_id = "<specify-target-table-sys-id>" # Replace with the target table sys_id
# Specify the file you want to attach
file_name = "igls-powerscale-share.xlsx"
file_path = f"/home/admin/{file_name}"
# Create a session for making authenticated requests
session = requests.Session()
session.auth = (username, password)
# Set proper headers
headers = {"Content-Type":"application/json","Accept":"application/json"}
# Set sysparm_limit
sysparm_query = f"file_name={file_name}"
# Check if an existing attachment exists and delete it
check_url = f'{rest_api_url}?sysparm_limit=2&sysparm_query={sysparm_query}'
existing_attachment_response = session.get(check_url, headers=headers)
if existing_attachment_response.status_code == 200:
existing_attachments = existing_attachment_response.json().get("result")
# Delete existing attachments
for attachment in existing_attachments:
if attachment.get("table_sys_id") == table_sys_id:
sys_id = attachment.get("sys_id")
delete_attachment_url = f"{rest_api_url}/{sys_id}"
delete_response = session.delete(delete_attachment_url)
if delete_response.status_code == 204:
print(f"Existing attachment with sys_id {sys_id} deleted.")
else:
print(f"Failed to delete existing attachment with sys_id {sys_id}. Status code: {delete_response.status_code}")
else:
print(f"Failed to check for existing attachment. Status code: {existing_attachment_response.status_code}")
print(existing_attachment_response.text)
# Send a POST request to upload the new file
new_attachment_url = f"{rest_api_url}/file?table_name={table_name}&table_sys_id={table_sys_id}&file_name={file_name}"
data = open(f'{file_path}', 'rb').read()
response = session.post(new_attachment_url, headers=headers, data=data)
# Check if the request was successful
if response.status_code == 201:
attachment_info = response.json().get("result")
sys_id = attachment_info.get("sys_id")
print(f"Attachment uploaded successfully. sys_id: {sys_id}")
else:
print(f"Failed to upload attachment. Status code: {response.status_code}")
print(response.text)
=========
igls-snapi-export.py
=====
import requests
# Replace these with your own ServiceNow instance details and credentials
instance_url = "https://<servicenow-instance-name>.service-now.com" # Specify ServiceNow instance URL
username = "<servicenow-user-api>" # specify user to execute this api
password = "<servicenow-password-api>" # specify user password to execute this api
# Set the URL for the ServiceNow REST API
rest_api_url = f"{instance_url}/api/now/attachment"
# Specify the table and table_sys_id where you want to attach the file
table_name = "sys_data_source" # Replace with the target table name
table_sys_id = "<specify-target-table-sys-id>" # Replace with the target table sys_id
# Specify the file you want to attach
file_name = "igls-powerscale-export.xlsx"
file_path = f"/home/admin/{file_name}"
# Create a session for making authenticated requests
session = requests.Session()
session.auth = (username, password)
# Set proper headers
headers = {"Content-Type":"application/json","Accept":"application/json"}
# Set sysparm_limit
sysparm_query = f"file_name={file_name}"
# Check if an existing attachment exists and delete it
check_url = f'{rest_api_url}?sysparm_limit=2&sysparm_query={sysparm_query}'
existing_attachment_response = session.get(check_url, headers=headers)
if existing_attachment_response.status_code == 200:
existing_attachments = existing_attachment_response.json().get("result")
# Delete existing attachments
for attachment in existing_attachments:
if attachment.get("table_sys_id") == table_sys_id:
sys_id = attachment.get("sys_id")
delete_attachment_url = f"{rest_api_url}/{sys_id}"
delete_response = session.delete(delete_attachment_url)
if delete_response.status_code == 204:
print(f"Existing attachment with sys_id {sys_id} deleted.")
else:
print(f"Failed to delete existing attachment with sys_id {sys_id}. Status code: {delete_response.status_code}")
else:
print(f"Failed to check for existing attachment. Status code: {existing_attachment_response.status_code}")
print(existing_attachment_response.text)
# Send a POST request to upload the new file
new_attachment_url = f"{rest_api_url}/file?table_name={table_name}&table_sys_id={table_sys_id}&file_name={file_name}"
data = open(f'{file_path}', 'rb').read()
response = session.post(new_attachment_url, headers=headers, data=data)
# Check if the request was successful
if response.status_code == 201:
attachment_info = response.json().get("result")
sys_id = attachment_info.get("sys_id")
print(f"Attachment uploaded successfully. sys_id: {sys_id}")
else:
print(f"Failed to upload attachment. Status code: {response.status_code}")
print(response.text)
=====
Schedule jobs through Crontabs
We combine all the python scripts into a single python script for easier scheduling.
Example: servicenow.py
=================
import subprocess
subprocess.run("/opt/.pyenv/shims/python3 /home/admin/igls-convert-cluster.py", shell=True)
subprocess.run("/opt/.pyenv/shims/python3 /home/admin/igls-convert-node.py", shell=True)
subprocess.run("/opt/.pyenv/shims/python3 /home/admin/igls-convert-share.py", shell=True)
subprocess.run("/opt/.pyenv/shims/python3 /home/admin/igls-convert-export.py", shell=True)
subprocess.run("/opt/.pyenv/shims/python3 /home/admin/igls-snapi-cluster.py", shell=True)
subprocess.run("/opt/.pyenv/shims/python3 /home/admin/igls-snapi-node.py", shell=True)
subprocess.run("/opt/.pyenv/shims/python3 /home/admin/igls-snapi-share.py", shell=True)
subprocess.run("/opt/.pyenv/shims/python3 /home/admin/igls-snapi-export.py", shell=True)
==============================
As admin user, create a crontab
crontab -e
Example to schedule to run every 30 minutes
30 * * * * /opt/.pyenv/shims/python3 /home/admin/servicenow.py 2>&1 > /home/admin/mycronout.log
© Superna Inc